From the article: Research through Design projects in the health domain often involve collaborations of design and healthcare researchers. All partners have their own ideas and expectations with regard to what they consider valid ways to support their work. The evidence-based approach that dominates healthcare research differs from the ways that are common in design research, in which more iterative approaches are applied with focus on developing solutions to fit to the users and their context. The question that we address is twofold: a) How do differences in grounding approaches manifest themselves in projects where design and healthcare researchers collaborate? And b) How do project teams deal with these differences? We analyzed the grounding practices within ten Dutch research projects that address the development of e-health applications to support people as they grow older. All projects are collaborations of design and healthcare researchers and practice partners. We applied a multiple case study research approach in two series of interviews, with a cross-case interpretation after the first series of interviews to direct the second series. Differences in grounding approaches in the projects manifest themselves on four themes, each representing a spectrum: time, structure, control and position. These differences provided challenges, but were also used to strengthen the project.
DOCUMENT
Communities of Practice (CoPs) are social learning systems that can be, to a certain extent, designed. Wenger (1998) proposes the following paradox; “ no community can fully design the learning of another, but at the same time, no community can fully design its own learning” (p:234). My interpretation of Wenger’s statement is that learning environments such as CoPs need to be facilitated in their learning processes, but not their specific design. Approaching CoPs this way allows for the design of interventions that facilitate learning processes within a CoP rather than regulate them. However, empirical studies on facilitating internal processes of CoPs are sparse – most work is anecdotal. This means that one needs to look to other fields for guidance in order to discover how to facilitate CoPs in their learning. This paper describes part of a larger research project that asks the question whether communities of practice can be instituted in higher professional educational organizations as an effective method to facilitate participant learning (professional development) and stimulate new knowledge creation in the service of the organization. Using a more pragmatic approach to cultivating CoPs (Ropes, 2007) opens the possibility to use different theoretical perspectives in order to find and ground interventions that can facilitate learning in CoPs and which are typically used in organizational development trajectories based on learning (de Caluwe & Vermaak, 2002). In this paper I look at how theories of human resource development, workplace learning and social constructivism conceptualize learning and what type of environments promote this. I then map out community of practice theory along these fields in order to come to a synthesized conceptual framework, which I will use to help understand what specific interventions can be used for designing CoPs. Finally I propose several interventions based on the work done here. The main question I consider here can be formulated as follows; ‘what insight can Human Resource Development theories, Workplace Learning theories and Social Constructivist learning theory give in order to design interventions that facilitate internal processes of communities of practice?’
DOCUMENT

The complexity of analysing dynamical systems often lies in the difficulty to monitor each of their dynamic properties. In this article, we use qualitative models to present an exhaustive way of representing every possible state of a given system, and combine it with Bayesian networks to integrate quantitative information and reasoning under uncertainty. The result is a combined model able to give explanations relying on expert knowledge to predict the behaviour of a system. We illustrate our approach with a deterministic model to show how the combination is done, then extend this model to integrate uncertainty and demonstrate its benefits
DOCUMENT

Wat dragen creatieve onderzoeksmethodes bij aan vernieuwing binnen de zorg? We onderzoeken dit binnen tien projecten van het Create Health-programma van ZonMw. In deze projecten wordt kennis ontwikkeld over de toegevoegde waarde van creatieve manieren van werken bij e-health innovatie.
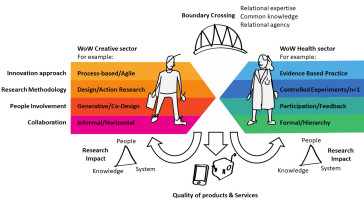
Wat dragen creatieve onderzoeksmethodes bij aan vernieuwing binnen de zorg? We onderzoeken dit binnen tien projecten van het Create Health-programma van ZonMw. In deze projecten wordt kennis ontwikkeld over de toegevoegde waarde van creatieve manieren van werken bij e-health innovatie. Informatie over de onderzoeksresultaten is te vinden op de website: husite.nl/creatieve-onderzoeksmethodes en het artikel: CHIWaWA maakt samenwerking in create-health onderzoek inzichtelijk | Hogeschool Utrecht (hu.nl)Doel Het Create Health programma heeft tot doel om bij te dragen aan maatschappelijke uitdagingen rondom gezond en actief ouder worden. CHIWaWA werkt daarbij toe naar een conceptueel model dat manieren van werken in kaart brengt in create health projecten – gekoppeld aan theorie over boundary crossing en research impact – met betrekking tot projectuitkomsten en kennis-, persoonlijke-, en systeemontwikkeling van betrokken actoren. Resultaten onderzoek Kennis die zowel online als offline te raadplegen is, in een boek, in wetenschappelijke artikelen en op een website. Deze kennis bevat: Inzicht in kansen om impact van e-health innovatie in ‘create health’-samenwerking te vergroten; Projectnarratieven met ‘best practices’ voor interdisciplinaire samenwerking waarbij onderzoekers, creatieve industrie en zorgprofessionals betrokken zijn; Guidelines voor ontwikkelaars van e-health applicaties m.b.t. samenwerking met de creatieve industrie; Guidelines voor beleidsmakers m.b.t. het stimuleren van samenwerking tussen zorg en creatieve industrie en het gebruik van creatieve manieren van werken om onderzoek naar de praktijk te krijgen; Aanpak Vanuit een service-dominant logic perspectief wordt bekeken hoe toegepaste kennis en skills worden gedeeld tussen actoren die betrokken zijn bij de verschillende ‘create health’-projecten, wat de meerwaarde daarvan is en wat actoren van die uitwisseling – als proces – leren. De focus ligt op co-creatie van waarde, die door samenwerking en uitwisseling tot stand komt. Door middel van procesonderzoek wordt er toegewerkt naar bijdragen aan theorieontwikkeling op het gebied van boundary crossing en contribution mapping. Resultaten Eindpublicatie: Create Health: Samenwerking tussen zorg, wetenschap en creatieve industrie (2023) Boek: Create Ways of Working. Insights from ten ehealth Innovation research projects (2022) Website www.creatieveonderzoeksmethodes.nl (2022) Bijdragen aan conferenties en symposia Co-design in de anderhalvemetermaatschappij (whitepaper), Dutch Design Week 2020. Download de presentatieslides. Collaborating in complexity. Strategies for interdisciplinary collaboration n design work, Design4Health conference 2020 Grounding Practices. How researchers ground their work in create-health collaborations for designing e-health solutions, Design4Health conference 2020 Seven ways to foster interdisciplinary collaboration in research involving healthcare and creative research disciplines, DementiaLab conference 2019 Posterpresentatie: Health x Design, DementiaLab conference 2019 Meer informatie over het Create Health programma Het ZonMw programma Create Health heeft als doel om bij te dragen aan de maatschappelijke uitdaging rondom gezond en actief ouder worden. Binnen het programma worden activiteiten uitgezet waarbij de samenwerking tussen de creatieve industrie en zorg en welzijn voorop staat. Het gaat hierbij om publiek-private samenwerking (PPS).
Vogels verspreiden zaden, bestuiven planten en ruimen de natuur op; ze zijn onmisbaar voor een gezond ecosysteem. Van groot maatschappelijk belang is het beschermen van bedreigde dieren; biodiversiteit zorgt voor een gezond klimaat in Nederland. Voor de bescherming van vogels worden nesten gedetecteerd en geregistreerd. Boeren worden vervolgens geïnformeerd over de aanwezigheid van nesten op hun land zodat ze de nesten niet vernietigen tijdens hun agrarische werkzaamheden. Boeren worden in Nederland gecompenseerd voor de bescherming van nesten waardoor economische belangen samenkomen met het behoud van de natuur. In dit project wordt met behulp van technologische innovatie de samenwerking tussen boeren en natuur- en vogelbescherming verstevigd: drones worden gecombineerd met artificiële intelligentie om in samenwerking met vrijwilligers de monitoring van nesten uit te voeren. Dit helpt de Bond Friese VogelWachten (BFVW) om met het huidige aantal vogelwachters meer nesten te kunnen opsporen, de natuur doordat meer detectie leidt tot hogere broedsucces van vogels, en de boer kan met de drone meer financiële compensatie bemachtigen. Het consortium bestaat uit BFVW, NHL Stenden Lectoraat Computer Vision & Data Science en het drone bedrijf Aeroscan, die gezamenlijk de technische haarbaarheid willen onderzoeken om de business-case te ondersteunen. Met deze technologie kan de BFVW efficiënter en vooral effectiever nesten in kaart brengen. In de toekomst worden de resultaten van dit project breder ingezet door dit consortium. Binnen natuurbehoud en biodiversiteit zijn er veel andere uitdagingen waarvoor de, in dit project ontwikkelde, kennis ingezet kan worden.