Urban nature enhancement is a theme that needs to be considered across different scales. From pocket parks and façade-greening to urban green infrastructure, biodiversity thrives best through connectivity.In the SIA-project, Nature-inclusive Area Development, four universities of applied sciences - Aeres University of Applied Sciences, Avans University of Applied Sciences, Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences, and Van Hall Larenstein University of AppliedSciences- researched three levels of area development to accelerate the transition to nature-inclusive area development. The study consisted of three case studies: Waarder Railway Zone (building), Knowledge Mile Park (KMP - street - Amsterdam), and AlmereCentre-Pampus (area).
DOCUMENT
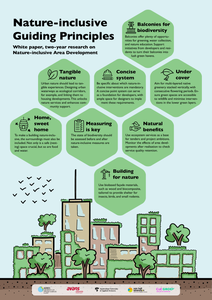
Stedelijke natuurversterking is bij uitstek een thema dat door de schalen heen moet worden bekeken. Van pocket park en gevelbekleding tot stedelijke groenstructuur, de biodiversiteit komt het beste tot bloei door samenhang.In het SIA-project Natuurinclusieve Gebiedsontwikkeling onderzochten vier hogescholen - Aeres Hogeschool, Avans Hogeschool, Hogeschool van Amsterdam en Hogeschool Van Hall Larenstein - drie schaalniveaus van gebiedsontwikkeling om de transitie naar natuurinclusieve gebiedsontwikkeling te versnellen. Gekoppeld aan drie casussen waren dit: gebouw (Spoorzone Waarder), straat (Knowledge Mile Park - KMP - Amsterdam), en gebied (Almere Centrum-Pampus). De casussen belichten veelvoorkomende typen ingrepen, zoals kleinschalige nieuwbouw, verbetering van de publieke ruimte, en binnenstedelijke woningbouw. Ondanks dat elke case een eigen thematisch zwaartepunt had - biobased materialen (Spoorzone Waarder), natuurlijke vergroening (KMP), en governance (Almere) - heeft via deelonderzoeken en tussen hogescholen kruisbestuiving plaatsgevonden. De white paper geeft de belangrijkste resultaten en lessen hiervan weer.Urban nature enhancement is a theme that needs to be considered across different scale levels. From pocket parks and façade greening to urban green infrastructure, biodiversity thrives best through connectivity.In the SIA-project Nature-inclusive Area Development, four universities of applied sciences - Aeres University of Applied Sciences, Avans UAS, Amsterdam UAS, and Van Hall Larenstein UAS- researched three scale levels of area development to accelerate the transition to nature-inclusive area development. This was linked to three case studies: Waarder Railway Zone (building), Knowledge Mile Park (KMP - street - Amsterdam), and Almere Centre-Pampus (area). The case studies represent common types of urban interventions, such as small-scale new developments, improvement of public space, and inner-city densification. Despite each case having its own thematic focus - biobased materials (Waarder Railway Zone), natural greening (KMP), and governance (Almere) - cross-pollination took place through sub-studies and collaboration between universities. The following pages present the main results and lessons learnt.
MULTIFILE

This paper seeks to highlight underlying issues of the tourism system that have led to tourism extremes of too much or too little tourism. Five phases are recognized that reflect different ways of dealing with too much tourism over time, after which the impact of a sudden lack of tourism is investigated in light of future renewal processes. This discussion highlights the remarkable capacity of the tourism industry to adjust to rapidly changing circumstances and crises, even when these cause anguish to individuals and within societies at large. The paper thus seeks to contextualize the current discussions regarding the transformation of tourism post COVID-19. It highlights the complexity of changing a tourism that multiple stakeholders depend on or have grown accustomed to. To come to a more balanced tourism, it is necessary to not only come up with alternative visions and strategies, but also to engage with the political economy nature of tourism development. A future research agenda should therefore also discuss facets of entangled power, social exclusion, inequalities and class differences to come to new reference points of what actually constitutes a more inclusive tourism success.
MULTIFILE

This paper analyses the initiative AgroAgenda in the northern Netherlands. The AgroAgenda is a platform in which multiple stakeholders together stimulate a circular, and nature-inclusive agro-food system in the Dutch provinces of Friesland, Groningen and Drenthe. Stakeholders come from, among others, provincial governments, farmers’ and nature organizations, educational and research institutes and processing companies. They join forces to realize a system change, a transition, in the region, while promoting knowledge circulation, knowledge co-creation and joint learning. The platform, is a front runner of five national, comparable initiatives. The AgroAgenda has the potential to lead to a more nature-inclusive and circular farming. Several of the 40 experiments have already led to good results. However, to bring about a real system change, more attention to innovations in governmental organizations (including law and regulations), policy, the value chains (division of margins, pricing and marketing) and the educational system are needed.
DOCUMENT

This paper essentially presents an exploration of the relationship between organizational culture and information systems management. Three contributions are offered namely the findings of a study of the organizational culture and information management competencies of five organizations in the Netherlands, with particular reference to the reliability of the measurements tool that was used, as well as an exploratory study of the relationship between organizational culture and the ability of an organization to manage its information systems. A brief review of the literature reveals that these two concepts in combination have been studied extensively, but that their conceptualization are somewhat fragmented in nature. In an effort to study the relationship using a more inclusive frame of reference the paper then presents a description of two models that were used the foundation for the design of a measurement tool to investigate the topic. The results provides a description of the general culture and information systems management abilities of the organizations and also suggest that the measurement tool is indeed reliable. Further analysis reveals that several variables from within each of the two main concepts, organizational culture and information systems management, are correlated.
DOCUMENT

Through the commodification of nature, the framing of the environment as a ‘natural resource’ or ‘ecosystem service’ has become increasingly prominent in international environmental governance. The economic capture approach is promoted by international organizations such as the United Nations Environmental Program (UNEP) through Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD), Payments for Ecosystem Services (PES) and The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity (TEEB). This paper will inquire as to how forest protection is related to issues of social and ecological justice, exploring whether forest exploitation based on the top-down managerial model fosters an unequitable distribution of resources. Both top-down and community-based approaches to forest protection will be critically examined and a more inclusive ethical framework to forest protection will be offered. The findings of this examination indicate the need for a renewed focus on existing examples of good practice in addressing both social and ecological need, as well as the necessity to address the less comfortable problem of where compromise appears less possible. The conclusion argues for the need to consider ecological justice as an important aspect of more socially orientated environmental justice for forest protection. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0376892916000436 https://www.linkedin.com/in/helenkopnina/
MULTIFILE

In this inaugural speech, Dr. Wertheim-Heck takes take you to themundane and often inconspicuous nature of our daily foodconsumption: our everyday fare. I believe that this holds animportant key for a successful transition towards a moresustainable, healthy and inclusive food system for the city. The author starts by giving a historical perspective with a personal slant. She then elaborates on the specific context of cities in transition towards a more sustainable, healthy, and inclusive food system. This will be linked to the specific context of Almere and the brief for the author's professorship within Food and Healthy living at Aeres University of Applied Sciences Almere
DOCUMENT

The Caribbean Netherlands are dealing with a situation where imported vegetables and fruits are mostly imported and hardly affordable. This leads to consuming unhealthy food and high obesities rates as a consequence. A lack of good agricultural practices with regard to water-smart and nature inclusive agriculture, as well as limited coping capacities to deal with hazards and climate change, results in very limited local production and interest. Initiatives that focused only on agrotechnological solutions for food resilient futures turned out to be ineffective due to a lack of local ownership, which jeopardizes sustainability. Moreover, the 'green' and 'blue' domains are not seen as attractive career perspectives among youth, hampering a bright future for those domains.
DOCUMENT

How can the stewards of our planet be rewarded and become an existential part of a brand-experience? Is our “Consumer mindset” actually able to always take our planet Earth’s viability in consideration while we’re consuming or buying products? Erwin van Woudenberg is a professor at HAS University of Applied sciences, leading a research program, Innovative Entrepreneurship in Rural Areas, aiming to develop new business models including nature-inclusive agriculture. Erwin comes up with unconventional solutions that inspire action, especially within agriculture and in connection with biodiversity and supply chains. He proudly tells us about his travels to the village of Lubuklinggau, on Sumatra, Indonesia where he is working on a rather revolutionary solution with Mr. Karmain. This farmer works on his rubber farm every day, while making decisions to either protect the forest or provide food for his family. This talk was given at a TEDx event using the TED conference format but independently organized by a local community.
LINK
We examine the demise of a multi-stakeholder network that was launched to promote an inclusive dairy market in Ethiopia to better understand why nongovernmental organizations (NGOs) may develop interventions in contexts of poverty that fail to endure after they exit. We identify organizational reflexivity – the capacity to recognize and understand the recursive interplay between an intervention and the local environment – as a key explanatory mechanism for this intervention outcome. Limited reflexivity not only prevented the NGO we studied from properly aligning the intervention with the context (design failures), but also prevented the organization from adjusting its intervention when negative feedback emerged (orchestration failures), which eventually evolved into the demise of the network (maintenance failure). While our study confirms the theoretical premise that NGOs need to contextualize their interventions, we expand current knowledge by highlighting the role of organizational reflexivity in this process. Moreover, by showing how reflexivity deficits can trigger a cascade of failure, especially when intervening in voids where incumbent firms have interests in maintaining the void, our study calls attention to the politicized nature of institutional voids.
DOCUMENT