Challenges that surveys are facing are increasing data collection costs and declining budgets. During the past years, many surveys at Statistics Netherlands were redesigned to reduce costs and to increase or maintain response rates. From 2018 onwards, adaptive survey design has been applied in several social surveys to produce more accurate statistics within the same budget. In previous years, research has been done into the effect on quality and costs of reducing the use of interviewers in mixed-mode surveys starting with internet observation, followed by telephone or face-to-face observation of internet nonrespondents. Reducing follow-ups can be done in different ways. By using stratified selection of people eligible for follow-up, nonresponse bias may be reduced. The main decisions to be made are how to divide the population into strata and how to compute the allocation probabilities for face-to-face and telephone observation in the different strata. Currently, adaptive survey design is an option in redesigns of social surveys at Statistics Netherlands. In 2018 it has been implemented in the Health Survey and the Public Opinion Survey, in 2019 in the Life Style Monitor and the Leisure Omnibus, in 2021 in the Labour Force Survey, and in 2022 it is planned for the Social Coherence Survey. This paper elaborates on the development of the adaptive survey design for the Labour Force Survey. Attention is paid to the survey design, in particular the sampling design, the data collection constraints, the choice of the strata for the adaptive design, the calculation of follow-up fractions by mode of observation and stratum, the practical implementation of the adaptive design, and the six-month parallel design with corresponding response results.
DOCUMENT

Accurate modeling of end-users’ decision-making behavior is crucial for validating demand response (DR) policies. However, existing models usually represent the decision-making behavior as an optimization problem, neglecting the impact of human psychology on decisions. In this paper, we propose a Belief-Desire-Intention (BDI) agent model to model end-users’ decision-making under DR. This model has the ability to perceive environmental information, generate different power scheduling plans, and make decisions that align with its own interests. The key modeling capabilities of the proposed model have been validated in a household end-user with flexible loads
DOCUMENT

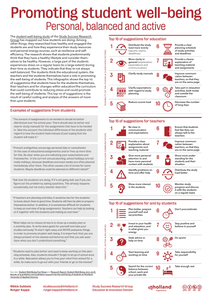
The student well-being study of the Study Success Research Group has mapped out how students are doing. Among other things, they researched how healthy and engaged the students are and how they experience their study resources and personal energy sources, such as resilience and selfefficiency. The research shows that students predominantly think that they have a healthy lifestyle and consider themselves to be healthy. However, a large part of the students experiences stress on a regular basis (to a large extent) during their time as students. This infographic shows the top 10 of suggestions that students have for the students themselves, their teachers and for changes within education/the curriculum that could contribute to reducing stress and could promote the well-being of students.
DOCUMENT
Author supplied from the article: Abstract A temperature compensated hydrogen sensor was designed and made capable of detecting H2 within a broad range of 100–10.000 ppm while compensating instantaneously for large (±25 °C) temperature variations. Two related operational constraints have been simultaneously addressed: (1) Selective, and sensitive detection under large temperature changes, (2) Fast warning at low and increasing H2 levels. Accurate measurements of hydrogen concentrations were enabled by matching relevant time-constants. This was achieved with a microchip having two temperature coupled palladium nanowires. One of the H2 sensitive Pd nanowires was directly exposed to hydrogen, whilst the other nanowire was used as a temperature sensor and as a reference. A drop forging technique was used to passivate the second Pd wire against H2 sensing. Temperature effects could be substantially reduced with a digital signal processing algorithm. Measurements were done in a test chamber, enabling the hydrogen concentration to be controlled over short and long periods. An early response for H2 sensing is attainable in the order of 600 milliseconds and an accurate value for the absolute hydrogen concentration can be obtained within 15 s.
LINK
Most higher education alumni work in professional fields, making higher education responsible for the provision of high-quality professionalism throughout society. However, higher education does not yet fulfil its role as a provider of methodologies for the renewal of professionalism. In this lecture, Didi Griffioen outlines the characteristics of professionalism, asserting that current methodologies for the continuous renewal of different elements of professionalism are lacking. By positioning itself as provider of these methodologies, higher education can play a more relevant role in society while also contributing to its own professional renewal and innovativeness.
DOCUMENT

"Probation is a fast-developing field that plays an important role in the response to crime and the prevention of reoffending. Probation covers various sanctions and community-based measures, including supervision and community service, designed to promote community safety and the social inclusion of offenders. This brochure is intended for justice ministers, other politicians and senior civil servants interested in setting up or upgrading a probation service. The ‘key message’ highlights the main topics and messages in this brochure. Readers who want to learn more about the benefits of probation and about how to bring these into practice should read the full text."
DOCUMENT

"Probation is a fast-developing field that plays an important role in the response to crime and the prevention of reoffending. Probation covers various sanctions and community-based measures, including supervision and community service, designed to promote community safety and the social inclusion of offenders. This brochure is intended for justice ministers, other politicians and senior civil servants interested in setting up or upgrading a probation service. The ‘key message’ highlights the main topics and messages in this brochure. Readers who want to learn more about the benefits of probation and about how to bring these into practice should read the full text."
DOCUMENT

Background: The proportion of frail older adults is increasing and is expected to further increase in the coming years, both globally and in the Dutch population. This poses a great challenge to public health. To determine the prevalence of frailty in a population, a frailty index (FI) is recommended. A FI is an accumulation model encompassing health deficits in multiple domains. Previous research has shown that a FI can be created out of existing health surveys, since it is a flexible instrument, fairly insensitive to the use of specific items. However, this is based on scale development using Classical Test Theory, while few studies have investigated the psychometric properties of their FI using Item Response Theory (IRT). The aim of this study was to create a FI using the Dutch Health Monitor 2016, and to investigate its psychometric properties using Item Response Theory (IRT). Methods: Forty-two deficits were selected in three health domains, i.e., physical, psychological, and social. Psychometric properties were investigated by using an IRT model for polytomous response categories: the Graded Response Model (GRM). Items were evaluated by Cronbach’s Alpha, Factor Analysis, Point Polyserial Correlations, and GRM. Results: The analyses showed that all items demonstrated a positive association with the scale. However, five items did not fit well to the FI scale. From the physical domain these were body mass index and three items about adherence to physical activity guidelines: moderate activity per week; bone and muscle strengthening activities; balance exercises. From the psychological domain this was an item about a sense of control over one’s own future. Conclusions: By using IRT, we showed that while 37 items were adequate and fitted the scale well, five items in our FI were redundant, indicating that it does matter which items are selected for a FI. IRT is a strong method for item selection and thus for creating a more concise Frailty Index. Key messages: Creating a solid and more concise Frailty Index with IRT is promising for epidemiological research and public health. For creating a Frailty Index, item selection needs careful consideration. [ABSTRACT FROM AUTHOR]
DOCUMENT
This paper seeks to highlight underlying issues of the tourism system that have led to tourism extremes of too much or too little tourism. Five phases are recognized that reflect different ways of dealing with too much tourism over time, after which the impact of a sudden lack of tourism is investigated in light of future renewal processes. This discussion highlights the remarkable capacity of the tourism industry to adjust to rapidly changing circumstances and crises, even when these cause anguish to individuals and within societies at large. The paper thus seeks to contextualize the current discussions regarding the transformation of tourism post COVID-19. It highlights the complexity of changing a tourism that multiple stakeholders depend on or have grown accustomed to. To come to a more balanced tourism, it is necessary to not only come up with alternative visions and strategies, but also to engage with the political economy nature of tourism development. A future research agenda should therefore also discuss facets of entangled power, social exclusion, inequalities and class differences to come to new reference points of what actually constitutes a more inclusive tourism success.
MULTIFILE

The performance of neural electrodes in physiological fluid, especially in chronic use, is critical for the success of functional electrical stimulation devices. Tips of the Utah electrode arrays (UEAs) were coated with sputtered iridium oxide film (SIROF) and activated iridium oxide film (AIROF) to study the degradation during charge injection consistent with functional electrical stimulation (FES). The arrays were subjected to continuous biphasic, cathodal first, charge balanced (with equal cathodal and anodal pulse widths) current pulses for 7 h (>1 million pulses) at a frequency of 50 Hz. The amplitude and width of the current pulses were varied to determine the damage threshold of the coatings. Degradation was characterized by scanning electron microscopy, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and cyclic voltammetry. The injected charge and charge density per phase were found to play synergistic role in damaging the electrodes. The damage threshold for SIROF coated electrode tips of the UEA was between 60 nC with a charge density of 1.9 mC/cm2 per phase and 80 nC with a charge density of 1.0 mC/cm2 per phase. While for AIROF coated electrode tips, the threshold was between 40 nC with a charge density of 0.9 mC/cm2 per phase and 50 nC with a charge density of 0.5 mC/cm2 per phase. Compared to AIROF, SIROF showed higher damage threshold and therefore is highly recommended to be used as a stimulation material.
DOCUMENT