Background Anxiety and challenging behaviour (CB) often occur simultaneously in people with intellectual disabilities (ID). Understanding the associations between anxiety and CB may contribute to more accurate diagnoses and management of both anxiety and CB in this population. Aims To examine the relationship between anxiety and CB. Methods A literature review covering the period from January 2000 to January 2012. Results Seven studies about the relationship between psychiatric disorders, including anxiety, and CB were identified. These studies confirm the relationship between anxiety and CB in people with ID, although the precise nature of this relationship remains unclear. Conclusions The study points toward the existence of a moderate association between anxiety and CB. Further research is needed to clarify the complex nature of the association between anxiety and CB.
DOCUMENT

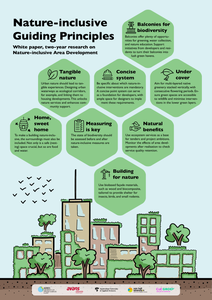
Urban nature enhancement is a theme that needs to be considered across different scales. From pocket parks and façade-greening to urban green infrastructure, biodiversity thrives best through connectivity.In the SIA-project, Nature-inclusive Area Development, four universities of applied sciences - Aeres University of Applied Sciences, Avans University of Applied Sciences, Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences, and Van Hall Larenstein University of AppliedSciences- researched three levels of area development to accelerate the transition to nature-inclusive area development. The study consisted of three case studies: Waarder Railway Zone (building), Knowledge Mile Park (KMP - street - Amsterdam), and AlmereCentre-Pampus (area).
DOCUMENT
In recent years, numerous environmental psychology studies have demonstrated that contact with nature as opposed to urban settings can improve an individual’s mood, can lead to increased levels of vitality, and can offer an opportunity to recover from stress. According to Attention Restoration Theory (ART) the restorative potential of natural environments is situated in the fact that nature can replenish depleted attentional resources. This replenishment takes place, in part, because nature is deemed to be a source of fascination, with fascination being described as having an ‘‘attentional’’, an‘‘affective’’ and an ‘‘effort’’ dimension. However, the claim that fascination with nature involves these three dimensions is to a large extent based on intuition or derived from introspection-based measurement methods, such as self-reports. In three studies, we aimed to more objectively assess whether these three dimensions indeed applied to experiences related to natural environments, before any (attentional) depletion has taken place. The instruments that were used were: (a) the affect misattribution procedure (Study 1), (b) the dot probe paradigm (Study 2) and (c) a cognitively effortful task (Study 3).These instrument were respectively aimed at verifying the affective, attentional and effort dimension of fascination. Overall, the results provide objective evidence for the claims made within the ART framework, that natural as opposed to urban settings are affectively positive (cfr., affective dimension) and that people have an attentional bias to natural (rather than urban) environments (cfr., attentional dimension). The results regarding the effort dimension are less straightforward, and suggest that this dimension only becomes important in sufficiently difficult cognitive tasks.
DOCUMENT

Almere is a green city where the greenery extends into the centre through a framework of nature, forests, parks and canals. With this green environment, Almere fulfils an important condition for a liveable city, where it is pleasant to live and work. An important goal for the municipality is to challenge its residents to develop a healthy lifestyle by using that green framework.But what really motivates Almeerders to go outside to exercise, enjoy the surroundings and meet each other? Are there sufficient green meeting or sports facilities nearby? Could the routes that connect the living and working environment with the larger parks or forests be better designed? And can those routes simultaneously contribute to climate adaptation?With the Green Escape Challenge, we invited students and young professionals to work on these assignments together.
DOCUMENT

This chapter is about the development of tourism in the Dutch Wadden Sea Region in combination with nature conservation. The main question is whether they have a common future. There are some future points stated:- Nature and landscape of the Wadden Sea are the main pull factors for the tourism development. - Future tourism development requires a clear strategy that is supported by various stakeholders- Raising awareness about the natural values results in more visitors and public support for nature conservation- The World Heritage status facilitates cooperation between local entrepreneurs and nature conservation organisationsOverall the conclusion can be drawn that, stimulated by the World Heritage status of the Wadden Sea and facilitated by a trilateral Sustainable Tourism Strategy, tourism development and nature conservation and can mutually benefit. Raising awareness about the natural values of the Wadden Sea will result in more visitors to the region and contributes to an emotional attachment to the protected area and public support for the conservation programs.
DOCUMENT

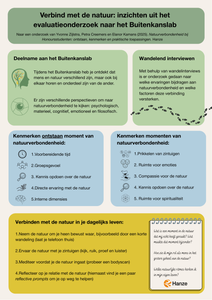
Naar een onderzoek van Yvonne Zijlstra, Petra Creemers en Elanor Kamans (2025). Natuurverbondenheid bij Honoursstudenten: ontstaan, kenmerken en praktische toepassingen.
DOCUMENT
The international Wadden Sea is an estuarine tidal area along the North Sea coasts of The Netherlands, Germany and Denmark. It is characteristic for regions with sandy coasts and a medium tidal range. Fifty barrier islands separate the Wadden Sea from the North Sea, and an offshore transition zone to the North Sea. The tidal flats of the Wadden Sea form the largest unbroken stretchof mudflats worldwide. The present form of the Wadden Sea is still mainly the result of natural forces, although since the Middle Ages man has changed the Wadden Sea landscape by building dykes and reclaiming land. The Wadden Sea is an important nursery area for fish, a foraging and resting habitat for seals, and a foraging habitat for migrating waders. The Wadden Sea, including large parts of the islands, is a fully nature protected area and designated as a natural World Heritage site in 2009 (Wolff, 2013). The research group Marine Wetlands Studies at Stenden University is focusing on the sustainable development of tourism in the area. Current research has the purpose to get insight in to the effects of the World Heritage Status, in particular the natural values of the area, on future tourism development.
DOCUMENT

This paper conceptualises tourist idleness as a temporary engagement in slow, slothful and entirely unstructured holiday activities. We aim to extend the studies that prioritise the modalities of holidays in nature that encourage simplified, slower, immersive experiences, and which celebrate mindfulness, slowness and stillness as part of a tourist journey. In framing idleness as a relaxing, creative and recuperative holiday practice, we suggest that creating places of otium which encourage ‘doing nothing’ can in many ways enhance tourist wellbeing. To this end, we discuss the significance of spatial, temporal and existential elements of tourist idleness, whilst arguing that this ‘practice’ should be more celebrated in our modern, high-speed societies.
MULTIFILE
A description how technology has alienated us from nature. The currentsocial-technical-ecological system (STES) tends to drive us towards techniques where connection with nature is more difficult. However, techniques can also play a role in restoring human–nature connectedness in (at least) two ways: (1) directly by restoring interest in nature through e.g. new materials, experiences, emotions and/or knowledge (case study 1 and 2); and (2) indirectly by organizing people around an environmental topic (case study 3). Citizen participation may help to counter this alienation and to accelerate the transition to sustainability. Finally, a reflection on the potential for designing technology that contributes to restoring human connectedness to nature or to the reinvention of our relationship with nature.
LINK
A description how technology has alienated us from nature. The currentsocial-technical-ecological system (STES) tends to drive us towards techniques where connection with nature is more difficult. However, techniques can also play a role in restoring human–nature connectedness in (at least) two ways: (1) directly by restoring interest in nature through e.g. new materials, experiences, emotions and/or knowledge (case study 1 and 2); and (2) indirectly by organizing people around an environmental topic (case study 3). Citizen participation may help to counter this alienation and to accelerate the transition to sustainability. Finally, a reflection on the potential for designing technology that contributes to restoring human connectedness to nature or to the reinvention of our relationship with nature.
LINK