This study theorizes on the sociomateriality of food in authority-building processes of partial organizations by exploring alternative food networks (AFNs). Through the construction of arenas for food provisioning, AFNs represent grassroots collectives that deliberately differentiate their practices from mainstream forms of food provisioning. Based on a sequential mixed-methods analysis of 24 AFNs, where an inductive chronological analysis is followed by a qualitative comparative analysis (QCA), we found that the entanglements between participants’ food provisioning practices and food itself shape how authority emerges in AFNs. Food generates biological, physiological and social struggles for AFN participants who, in turn, respond by embracing or avoiding them. As an outcome, most AFNs tend to bureaucratize over time according to four identified patterns while a few idiosyncratically build a more shared basis of authority. We conclude that the sociomateriality of food plays an important yet indirect role in understanding why and how food provisioning arenas re-organize and forge their forms of authority over time. Pascucci, S., Dentoni, D., Clements, J., Poldner, K., & Gartner, W. B. (2021). Forging Forms of Authority through the Sociomateriality of Food in Partial Organizations. Organization Studies, 42(2), 301-326. https://doi.org/10.1177/0170840620980232
DOCUMENT

Within eGovernment, trust in electronic stored information (ESI) is a necessity. In the last decades, most organizations underwent substantial reorganization. The integration of structured data in relational databases has improved documentation of business transactions and increased data quality. That integration has improved accountability as well. Almost 90% of the information that organizations manage is unstructured (e.g., e-mail, documents, multimedia files, etc.). Those files cannot be integrated into a traditional database in an easy way. Like structured data, unstructured ESI in organizations can be denoted as records, when it is meant to be (and used as) evidence for organizational policies, decisions, products, actions and transactions. Stakeholders in eGovernment, like citizens, governments and courts, are making increasing demands for the trustworthiness of this ESI for privacy, evidential and transparency reasons. A theoretical analysis of literature of information, organization and archival science illustrates that for delivering evidence, reconstruction of the past is essential, even in this age of information overload. We want to analyse how Digital Archiving and eDiscovery contribute to the realization of trusted ESI, to the reconstruction of the past and to delivering evidence. Digital Archiving ensures (by implementing and managing the ‘information value chain’) that: [1] ESI can be trusted, that it meets the necessary three dimensions of information: quality, context and relevance, and that [2] trusted ESI meets the remaining fourth dimension of information: survival, so that it is preserved for as long as is necessary (even indefinitely) to comply to privacy, accountability and transparency regulations. EDiscovery is any process (or series of processes) in which (trusted) ESI is sought, located, secured and searched with the intent of using it as evidence in a civil or criminal legal case. A difference between the two mechanisms is that Digital Archiving is implemented ex ante and eDiscovery ex post legal proceedings. The combination of both mechanisms ensures that organizations have a documented understanding of [1] the processing of policies, decisions, products, actions and transactions within (inter-) organizational processes; [2] the way organizations account for those policies, decisions, products, actions and transactions within their business processes; and [3] the reconstruction of policies, decisions, products, actions and transactions from business processes over time. This understanding is extremely important for the realization of eGovernment, for which reconstruction of the past is an essential functionality. Both mechanisms are illustrated with references to practical examples.
DOCUMENT

This thesis describes an Action Research (AR) project aimed at the implementation of Evidence Based Practice in a mental health nursing setting in the Netherlands. The main research question addressed in this thesis is: In what way is Action Research with an empowering appropriate to implement Evidence Based Practice in a mental health nursing setting in the Netherlands and what is the effect of this implementation on the care experienced by the client, the nursing interventions and the context in this setting compared to a comparative setting? To answer this main research question, the following questions derived from it were addressed: What is Evidence Based Practice? What is known about implementing evidence-based practice in nursing through Action Research? Which factors have to be dealt with in a mental health nursing setting, so the implementation of EBP with AR with an empowering intent will be more successful? Which factors have to be dealt with in a mental health nursing setting, so the implementation of EBP with AR with an empowering intent will be successful? How is EBP implemented through AR with an empowering intent and what are the outcomes for the use of evidence, the context and the facilitation in the setting? What is the effect of the implementation of EBP in mental health nursing using AR with an empowering intent on the care experienced by the client, the nursing interventions and the context compared to a comparison setting? The first two questions were answered by a search of the literature while the remaining questions were answered during the AR study conducted in two mental health organisations in the Netherlands.
DOCUMENT

Vind jij het ook een uitdaging om onderwijsinnovaties om te zetten tot veranderingen in de onderwijspraktijk? Wil je niet alleen beter begrijpen wat onderwijsinnovatie zo moeilijk maakt, maar ook samen op zoek gaan naar oplossingen? Kom dan naar de innovatiewerkplaats, een project van lectoraat Organiseren van Verandering in Onderwijs en het Teaching and Learning Network. Open voor alle onderwijsprofessionals (binnen en buiten de HU).
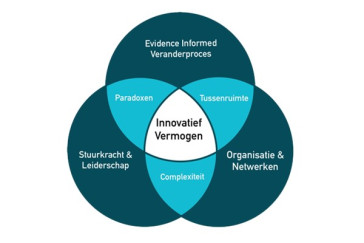
Het kennisnetwerk “Leren en Ontwikkelen voor Toekomstgericht Onderwijs” richt zich op onderwijsvernieuwingsvraagstukken. Scholen staan voor complexe uitdagingen waaronder een toename in diversiteit aan leerlingen die maatwerk vragen, de hardnekkige kansenongelijkheidsproblematiek, de noodzaak nieuwe technologieën adequaat in te zetten, en de opdracht leerlingen nieuwe leerinhouden maar vooral nieuwe leervaardigheden aan te leren. Voor scholen leidt dit tot aanpassingen zoals afstappen van klassikaal werken, focussen op leerprocessen in plaats van leerproducten en inzetten op autonomievergroting bij leerlingen. Onafhankelijk van de sector kampen scholen met vergelijkbare (ontwikkel)vraagstukken zoals nieuwe (meer ontwerpende en coachende) rollen van leraren, het anders beoordelen en monitoren van leerlingen en nieuwe samenwerkingsvormen binnen teams. Ons kennisnetwerk omvat bestaande samenwerkingsverbanden van lerarenopleidingen en scholenclusters die ervaring hebben met gezamenlijk onderzoek doen, opleiden en professionaliseren. De lectoren kennen elkaar van gemeenschappelijke (praktijkgerichte) onderzoeksprojecten, professionaliseringsactiviteiten en onderwijsontwikkeling. In het kennisnetwerk brengen we de verschillende samenwerkingsverbanden fysiek samen doordat onderzoekers, (toekomstige) leraren en lerarenopleiders in kennislabs op een onderzoeksmatige manier werken aan praktische oplossingen voor eerdergenoemde vraagstukken. Daarbij wordt gebruik gemaakt van een methodiek voor hybride kennislabs, ontwikkeld door een van de lectoraten, samen met de OU. Binnen het netwerk is een kernteam verantwoordelijk voor enerzijds destillatie van prangende onderzoeksvragen en het doen van onderzoeksaanvragen en anderzijds de monitoring van zowel de leeropbrengsten als praktische opbrengsten (werkzame principes) van de kennislabs en de verfijning van de werkwijze binnen de kennislabs. Het uiteindelijke doel zijn kennislabs die zodanig regionaal verankerd zijn wat betreft de professionalisering van betrokkenen, kennisdeling, inspiratie en ondersteuning bij het ontwikkelen van toekomstgericht onderwijs en het aanvragen en uitvoeren van praktijkgericht onderzoek dat deze na vier jaar zonder subsidie kunnen worden voortgezet. Daarnaast vormen ze een onmisbaar onderdeel van een landelijke kennisinfrastructuur. We beogen een open netwerkorganisatie waarbij lerarenopleidingen, scholen en kennisinstellingen zich op basis van hun expertise kunnen aansluiten
How can European migration, between countries and within countries between regions, contribute to the development of vulnerable regions in Europe? This is the central question of project Premium_EU (Policy REcommendations to Maximise the beneficial Impact of Unexplored Mobilities in and beyond the European Union), which is financed by Horizon Europe.The key goal of Premium_EU is the development of a Regional Policy Dashboard for national and regional policy makers to help them in the formulation of new policies aimed at the potential of migration to enhance the development of vulnerable regions. The Dashboard combines all available knowledge of three domains in three modules: the Mobility Module, the Regional Development Effects Module, and the Policy Module.The Mobility Module includes both past trends and projections and scenarios, in addition to new mobility estimates based on data from social media usage, such as LinkedIn and Facebook. The module also includes qualitative information from case studies on specific types of mobility groups, such as Polish seasonal workers, or Turkish migrants to EU countries. These trends, projections and case studies will be summarized in a regional typology on the basis of the mobility profile of the region.In the Regional Development Effects Module all available data on regional development is summarized in a regional development typology, where regional development is interpreted much broader than economic development. Using causal models the role of regional mobility in regional development will be established.In the Policy Module all possible forms of regional policies will be collected and linked to the mobility- and regional development characteristics of the region.The Dashboard integrates these modules so that a policy maker, on the basis of the unique mobility and regional development profile of his or her region is able to make an evidence based choice out of a relevant set of policy options. Users of the Dashboard will also be able to add their experiences to the Dashboard, so that other users can benefit from their knowledge.