Podcast over 2 van de 12 guiding principles die zijn voortgekomen uit COP4HL project.
LINK
The free market underpins our economy and our way of thinking around enterprise and value, but it is also a major factor in the sustainability problems that we now live with. Climate change, child labour and oil spills are just a few of the many problems associated with our economic activity and, although many companies have made an effort to produce more sustainably, the pace of change is much too slow. This engaging and accessible textbook teaches students the relationship between the economy and sustainability, assessing the hand of the free market on company behaviour and, ultimately, providing a framework for transition to a sustainable economy. Using case studies and optional assessment questions, this textbook explains to students what a market is at the macro level and then translates the effects of the market to industries and subsequently to the strategic choices of companies at the micro level. It adopts a model of 8 guiding principlesthat underpin the current free market economy and 8 guiding principles for the sustainable market economy. Switching these deeply held principles will be essential to any serious transition to a sustainable economy.
DOCUMENT
Developing students’ information problem solving (IPS) competence in higher education is imperative. However, existing theoretical frameworks describe IPS learning outcomes without guiding effective learning environment design. This systematic review and meta-analysis synthesized empirical evidence to formulate design principles for developing IPS competence. A systematic search across seven academic databases yielded 69 peer-reviewed articles from 2000–2023 with controlled pretest-posttest designs targeting (under)graduate students. Analysis of these studies yielded seven design principles: learning task, instruction, modeling, practice, learning activities, support, and feedback, with meta-analyses validating key relationships. The IPS educational design principles (IPS-EDP) model summarizes how these principles address learning outcomes, teaching and learning activities, and assessment strategies. While our review covered all IPS components, empirical evidence predominantly addressed information search and selection,
MULTIFILE
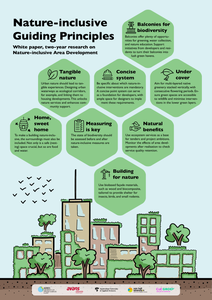
Urban nature enhancement is a theme that needs to be considered across different scales. From pocket parks and façade-greening to urban green infrastructure, biodiversity thrives best through connectivity.In the SIA-project, Nature-inclusive Area Development, four universities of applied sciences - Aeres University of Applied Sciences, Avans University of Applied Sciences, Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences, and Van Hall Larenstein University of AppliedSciences- researched three levels of area development to accelerate the transition to nature-inclusive area development. The study consisted of three case studies: Waarder Railway Zone (building), Knowledge Mile Park (KMP - street - Amsterdam), and AlmereCentre-Pampus (area).
DOCUMENT
What do human rights look like when we present them as action-based, bottom-up concepts, and not exclusively as legal items? After all, when we narrow down human rights to a legal concept only, we do not do justice to its meaning. In many professions and branches the idea of human rights is used in jargon, as guiding principles and as a source of inspiration. Human rights make a difference, albeit not necessarily as an enforceable legal concept. This facet of human rights - its practical application beyond lawmakers and lawyers - is deeply underexplored and deserves much more attention. Applied human rights are not per se a matter of lawmaking and enforcement only: it can be part of a mission and vision of companies, it is sometimes at the core of artistic work, it can be a leading principle in social work - especially considering the rights of the child, and it is used as a guiding principle in technological innovation. Human rights are not just for lawyers, but also for managers, engineers, social workers, musicians, local governments, law enforcers, designers and business people. However, and not surprisingly, in each branch the impact and implications of human rights differ. Therefore, it is time for a comprehensive textbook in which the idea of human rights is not exclusively explored as a legal concept, but instead discussed from various applied perspectives. In this book, we explore human rights as an applied concept: as something we do. The chapters are written by an international group of leading experts in a wide range of disciplines and themes, including technology development, social studies, pedagogy, business strategy, public governance, the arts, philosophy and law.
LINK
Developing students’ information problemsolving (IPS) competence in higher education is imperative. However, existing theoretical frameworks describe IPS learning outcomes without guiding effective learning environment design. This systematic review and meta-analysis synthesized empirical evidence to formulate design principles for developing IPS competence. A systematic search across seven academic databases yielded 69 peer-reviewed articles from 2000–2023 with controlled pretest-posttest designs targeting (under)graduate students. Analysis of these studies yielded seven design principles: learning task, instruction, modeling, practice, learning activities, support, and feedback, with meta-analyses validating key relationships. The IPS educational design principles (IPS-EDP) model summarizes how these principles address learning outcomes, teaching and learning activities, and assessment strategies. While our review covered all IPS components, empirical evidence predominantly addressed information search and selection, potentially limiting generalizability to broader IPS competence. The IPSEDP model provides a theoretical foundation for investigating and designing effective IPS learning environments in higher education, bridging research and practice.
LINK
Considering the challenges on sustainable agriculture in the district, different institutions join hands to overcome these issues and respond to the felt need of working more integrative both in the agricultural sector and environmental knowledge system. Adding a sense of urgency due to COVID-19 into problem analysis, these institutions accelerated the ambition to develop a Digital Farmer Field School (DFFS). This paper elaborates on the co-construction of principles for the design of a Digital Farmer Field School (DFFS) by the local stakeholders in Enrekang district. The local design team design of the DFFS Enrekang is composed of a transdisciplinary team from relevant government institutions and research institutions. The design principles of DFFS are built around inclusive design principles, concepts of interface usability based on different type of access to digital technology models, responsible innovation criteria and learning principles of farmer field school (FFS). The DFFS Enrekang design principles serve as guiding principles and shared value among the collaborating institutions to combine ambition, inspiration, and accountability in the DFFS management and development processes. This tablet based digital learning platform aims to provide an alternative for farmers to access information on sustainable agricultural and environmental practices.
DOCUMENT

Business decisions and business logic are important organizational assets. As transparency is becoming an increasingly important aspect for organizations, business decisions and underlying business logic, i.e., their business rules, must be implemented, in information systems, in such a way that transparency is guaranteed as much as possible. Based on previous research, in this study, we aim to identify how current design principles for business rules management add value in terms of transparency. To do so, a recently published transparency framework is decomposed into criteria, which are evaluated against the current business rules management principles. This evaluation revealed that eight out of twenty-two design principles do not add value to transparency, which should be taken into account when the goal of an organization is to increase transparency. Future research should focus on how to implement the design principles that add to transparency.
DOCUMENT

The relevance of an internationalised home curriculum for all students is generally acknowledged. Other than study abroad, the home curriculum gives programs of study full control over the way students learn international, intercultural, and interdisciplinary perspectives. However, misconceptions, lack of strategies, lack of skills of academics, and lack of connection between stakeholders present major obstacles to internationalising teaching and learning “at home”. The practical trajectory outlined in this chapter presents programs of study with the opportunity to focus on employability skills instead of on a semantic discussion on internationalisation. By linking this orientation on employability skills with the articulation of intended learning outcomes (ILOs), a pathway for developing employability skills in all students will be created. Within this pathway, international, intercultural, interdisciplinary, and future-focused dimensions serve to enhance students’ acquiring employability skills. The trajectory presented here evolved out of action research on internationalisation with academics. During the action research, taking employability skills as a starting point emerged as an enabler for the internationalisation process. It helped to overcome lengthy and semantic discussions on the meaning of internationalisation. After that, international and intercultural dimensions are included in these employability skills. These skills are then translated into ILOs. This is an Accepted Manuscript of a book chapter published by Routledge/CRC Press in Internationalization and employability in higher education on 19/25/06, available online: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/e/9781351254885.
MULTIFILE

From the article: "Abstract, technology-enhanced learning can be used to replicate existing teaching practices, supplement existing teaching or transform teaching and/or learning process and outcomes. Enhancing workplace learning, which is integrated into higher professional education, with technology, calls for designing such transformations. Although research is carried out into different kinds of technological solutions to enhance workplace learning, we do not know which principles should guide such designs. Therefore, we carried out an explorative, qualitative study and found two such design principles for the design of technology-enhanced workplace learning in higher professional education. In this research, we focused on the students' perspective, since they are the main users of such technology when they are learning at the workplace, as part of their study in becoming lifelong learning, competent professionals."
DOCUMENT
