One of the work packages which Hanzehogeschool emphatically has a role, is Research and Training. In the Summer Academy teachers are trained by translating their knowledge back to their own schools.The Summer Academy is given on 27-30 May 2013, as part of "Opening Up". This project aims to find better service to citizens and businesses through the use of social media and open data. The opening-up project started in October 2011 and lasts three years. Hanze University Groningen is an important partner in the project.
DOCUMENT

One of the work packages which Hanzehogeschool emphatically has a role, is Research and Training. In the Summer Academy teachers are trained by translating their knowledge back to their own schools.The Summer Academy is given on 27-30 May 2013, as part of "Opening Up". This project aims to find better service to citizens and businesses through the use of social media and open data. The opening-up project started in October 2011 and lasts three years. Hanze University Groningen is an important partner in the project.
DOCUMENT
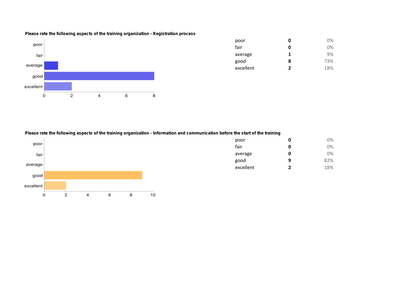
OpeningUp is een project dat voortvloeit uit ‘The Interreg IVB North Sea Region Programme’. Een Europees subsidieprogramma dat zichzelf tot doel stelt het leven en werken in de Noordzee Regio aantrekkelijker te maken en transnationale samenwerking te bevorderen. Dit doet zij onder andere door het stimuleren van initiatieven op het gebied van open data en social media in de verwachting dat economische ontwikkeling in de regio zal toenemen. Het project wordt in grote lijnen beschreven: achtergrond en aanleiding, projectdoel en geplande resultaat en de betrokken disciplines en belanghebbenden. Dit mede in relatie met de bedrijfskundige aspecten als strategie, interne organisatie en diagnose.
DOCUMENT

First year students Aeronautical Engineering had the opportunity to enter a five days program to enhance their mathematical skills. The program had 55 participants. Our research questions were: What are the effects of participation in the summer school program on math skills? Do participants experience more motivation and academic self-esteem after participation? Do dropout rates differ between participating and non-participating students? Do participants differ from non-participating students in motivation or academic self-esteem? We presented the results at the European First Year Experience in Cork, Ireland.
DOCUMENT

Purpose: Adolescents are insufficiently physically active and spent too much time sitting, which provides a health risk. In the current study the municipality of Amsterdam, secondary schools, experts in urban sports and researchers work together to stimulate healthy exercise behavior of adolescents. The urban sports facilities in the city of Amsterdam are at the center of this project. A variety of urban sports facilities have been realized over the last years. It remains however unknown which adolescents actually use these facilities. When urban space planning and physical education (PE) lessons at school are aligned and adjusted to the needs and preferences of adolescents, adolescents probably feel more competent to use the urban sport facilities surrounding their schools. The goal of this project is twofold: 1) findings working principles for designing urban sports facilities in the urban space surrounding schools 2) identifying elements in secondary school physical education lessons that motivate adolescents to use the urban sports facilities.Methods: This was investigated by applying design thinking methods and co creation sessions with adolescents, PE teachers, school boards, municipality and experts in urban sports.Results: First results indicate that needs, wishes and barriers of adolescents with regard to the use of urban sports facilities are currently insufficiently documented. Moreover, physical education teachers lack a feeling of competence in providing urban sports classes and there is insufficient coordination between schools, the municipality and providers of urban sports. Next steps in the design thinking cycle will be discussed as well as implications for the municipality with regard to planning of urban sports facilities around school, and how to connect physical education programming inside and outside secondary schools.
MULTIFILE

Kick-Start College is a three-day pre-academic program (summer school) for prospective first year students of Inholland Rotterdam, University of Applied Sciences. The aim is to integrate students academically and socially, which could make the transition to higher education easier and eventually lead to lower dropout rates of students. Research has been conducted on both student experiences with the program as well as effects of the program. Method: pretest-posttest with academic-, social-, professional- and university integration1, self-esteem, motivation, evaluation.
DOCUMENT

Background: The worldwide increase in the rates of childhood overweight and physical inactivity requires successful prevention and intervention programs for children. The aim of the Active Living project is to increase physical activity and decrease sedentary behavior of Dutch primary school children by developing and implementing tailored, multicomponent interventions at and around schools. Methods/design: In this project, school-centered interventions have been developed at 10 schools in the south of the Netherlands, using a combined top-down and bottom-up approach in which a research unit and a practice unit continuously interact. The interventions consist of a combination of physical and social interventions tailored to local needs of intervention schools. The process and short- and long-term effectiveness of the interventions will be evaluated using a quasi-experimental study design in which 10 intervention schools are matched with 10 control schools. Baseline and follow-up measurements (after 12 and 24 months) have been conducted in grades 6 and 7 and included accelerometry, GPS, and questionnaires. Primary outcome of the Active Living study is the change in physical activity levels, i.e. sedentary behavior (SB), light physical activity (LPA), moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA), and counts-per-minute (CPM). Multilevel regression analyses will be used to assess the effectiveness of isolated and combined physical and social interventions on children’s PA levels. Discussion: The current intervention study is unique in its combined approach of physical and social environmental PA interventions both at school(yard)s as well as in the local neighborhood around the schools. The strength of the study lies in the quasi-experimental design including objective measurement techniques, i.e. accelerometry and GPS, combined with more subjective techniques, i.e. questionnaires, implementation logbooks, and neighborhood observations. LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/sanned/
DOCUMENT

Doel van het onderzoek is om meer inzicht te krijgen in de summerschools van Inholland, waaronder op het gebied van omvang, doel, vormgeving en gepercipieerde effecten. Hierdoor zouden summerschools van elkaar kunnen leren en de eigen summerschool kunnen optimaliseren. Op basis van een semigestructureerd interview met vertegenwoordigers van de summerschools is een beschrijving van elke summerschool gemaakt. In deze rapportage worden de beschrijvingen weergegeven, met als doel anderen te inspireren en van elkaar te leren. De opzet en uitkomsten van het onderzoek worden weergegeven in het rapport van Knuiman en Kappe1 (2017). Daarin is ook een analyse van de beschrijvingen opgenomen.
DOCUMENT

Between 1 March 2021 and 30 April 2023, a consortium (consisting of in the Netherlands: the National Library of the Netherlands (Koninklijke Bibliotheek -KB), The Hague University of Applied Sciences, the Netherlands Institute for Sound and Vision in Hilversum; in Belgium: Media & Learning Association in Leuven and Public Libraries 2030 in Brussels; and in Spain: Fundación Platoniq in Barcelona) carried out an Erasmus+-funded research project on news media literacy among young people. It involved Dutch, Belgian and Spanish young people aged 12-15. The acronym SMILES, which stands for 'innovative methodS for Media & Information Literacy Education involving schools and librarieS', was chosen for the project title. The main goals of the SMILES project are: • Forming pairs between librarians and secondary school teachers in the three European countries, who were empowered through train-the-trainer workshops to teach secondary school students about news media literacy in relation to disinformation; • Helping students use digital technologies more safely and responsibly with a focus on recognising reliable and authentic information versus becoming more resilient to disinformation; • Developing five building blocks serving as teaching materials for Dutch, Belgian and Spanish pupils aged 12-15 with the aim of making them recognise disinformation and making them more resilient against it; • A scientific evaluation of the effectiveness of the implemented lessons through impact measurement using 'pre-knowledge tests' and 'post-knowledge tests'; • A strengthening of existing collaborations and creation of new collaborations between schools and libraries in the three partner countries. The SMILES project was implemented through three work packages. In the first work package, five so-called 'Baseline studies', or literature reviews, were conducted. The focus was on what the different educational approaches in Spain, Belgium and the Netherlands are with regard to disinformation and how these approaches can be linked. Based on these studies, the five building blocks were developed in the second work package. In addition, the teaching pairs were offered the training programme developed by SMILES through a 'train-the-trainer methodology' to safely and responsibly deploy the use of digital media tools during lessons with students. Also, based on the disinformation literature, the knowledge tests were designed to conduct an impact measurement of the train-the-trainer workshops and lessons among the trainers (teaching pairs) and students, respectively. These knowledge tests contained statements on disinformation that were answered correctly or incorrectly by respondents. The number of correctly answered statements prior to the lessons was compared with the number of correctly answered statements after the lessons. In this way, an attempt was made to prove a positive learning effect of the deployed lessons. In the third work package, the results from the pre-knowledge tests and the post-knowledge tests were analysed. In addition to these quantitative analyses, qualitative results were also used to analyse and look at the extent to which the training provided to trainers (teaching pairs) and the lessons with the five building blocks for students proved effective in teaching, recognising and becoming more resilient to disinformation, respectively. In doing so, we also reflect on whether the methodology tested has been effective in the three countries: what are the best practices and where do we see areas for improvement?
DOCUMENT
