Schepen in moeilijkheden op zee leveren vaak besluitvormingsproblemen op tussen de scheepseigenaar/kapitein en de kuststaat. Kuststaten en met name de lokale overheden willen een probleem schip graag zo ver mogelijk weg sturen van hun gebied terwijl de eigenaar/kapitein zijn schip graag zo snel mogelijk naar de kust, een beschutte locatie of haven wil brengen. Het onderzoek geeft onderbouwing voor de besluitvorming rond schepen in moeilijkheden, zowel voor de zeescheepvaart als de betrokken besluitvormers van oeverstaten. Het product van het project is: een, op uitgewerkte scenario’s per scheepstype en lading gebaseerde besluitvormingsprocedure voor zeeschepen in moeilijkheden

Steeds meer jongeren in grote steden kampen met omstandigheden die hen overweldigen. Soms weten ze zich daaruit te ontworstelen en krijgen ze zicht op een beter leven. Positieve emoties en succeservaringen zijn daarbij cruciaal, blijkt uit het recente promotieonderzoek van Sebastian Abdallah in Beiroet en Amsterdam. Wat betekent dit voor de recente gewelddadige gebeurtenissen in Amsterdam?
LINK
Wat dragen creatieve onderzoeksmethodes bij aan vernieuwing binnen de zorg? We onderzoeken dit binnen tien projecten van het Create Health-programma van ZonMw. In deze projecten wordt kennis ontwikkeld over de toegevoegde waarde van creatieve manieren van werken bij e-health innovatie.
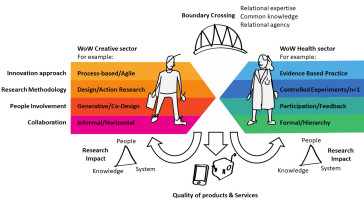
Wat dragen creatieve onderzoeksmethodes bij aan vernieuwing binnen de zorg? We onderzoeken dit binnen tien projecten van het Create Health-programma van ZonMw. In deze projecten wordt kennis ontwikkeld over de toegevoegde waarde van creatieve manieren van werken bij e-health innovatie. Informatie over de onderzoeksresultaten is te vinden op de website: husite.nl/creatieve-onderzoeksmethodes en het artikel: CHIWaWA maakt samenwerking in create-health onderzoek inzichtelijk | Hogeschool Utrecht (hu.nl)Doel Het Create Health programma heeft tot doel om bij te dragen aan maatschappelijke uitdagingen rondom gezond en actief ouder worden. CHIWaWA werkt daarbij toe naar een conceptueel model dat manieren van werken in kaart brengt in create health projecten – gekoppeld aan theorie over boundary crossing en research impact – met betrekking tot projectuitkomsten en kennis-, persoonlijke-, en systeemontwikkeling van betrokken actoren. Resultaten onderzoek Kennis die zowel online als offline te raadplegen is, in een boek, in wetenschappelijke artikelen en op een website. Deze kennis bevat: Inzicht in kansen om impact van e-health innovatie in ‘create health’-samenwerking te vergroten; Projectnarratieven met ‘best practices’ voor interdisciplinaire samenwerking waarbij onderzoekers, creatieve industrie en zorgprofessionals betrokken zijn; Guidelines voor ontwikkelaars van e-health applicaties m.b.t. samenwerking met de creatieve industrie; Guidelines voor beleidsmakers m.b.t. het stimuleren van samenwerking tussen zorg en creatieve industrie en het gebruik van creatieve manieren van werken om onderzoek naar de praktijk te krijgen; Aanpak Vanuit een service-dominant logic perspectief wordt bekeken hoe toegepaste kennis en skills worden gedeeld tussen actoren die betrokken zijn bij de verschillende ‘create health’-projecten, wat de meerwaarde daarvan is en wat actoren van die uitwisseling – als proces – leren. De focus ligt op co-creatie van waarde, die door samenwerking en uitwisseling tot stand komt. Door middel van procesonderzoek wordt er toegewerkt naar bijdragen aan theorieontwikkeling op het gebied van boundary crossing en contribution mapping. Resultaten Eindpublicatie: Create Health: Samenwerking tussen zorg, wetenschap en creatieve industrie (2023) Boek: Create Ways of Working. Insights from ten ehealth Innovation research projects (2022) Website www.creatieveonderzoeksmethodes.nl (2022) Bijdragen aan conferenties en symposia Co-design in de anderhalvemetermaatschappij (whitepaper), Dutch Design Week 2020. Download de presentatieslides. Collaborating in complexity. Strategies for interdisciplinary collaboration n design work, Design4Health conference 2020 Grounding Practices. How researchers ground their work in create-health collaborations for designing e-health solutions, Design4Health conference 2020 Seven ways to foster interdisciplinary collaboration in research involving healthcare and creative research disciplines, DementiaLab conference 2019 Posterpresentatie: Health x Design, DementiaLab conference 2019 Meer informatie over het Create Health programma Het ZonMw programma Create Health heeft als doel om bij te dragen aan de maatschappelijke uitdaging rondom gezond en actief ouder worden. Binnen het programma worden activiteiten uitgezet waarbij de samenwerking tussen de creatieve industrie en zorg en welzijn voorop staat. Het gaat hierbij om publiek-private samenwerking (PPS).
Vogels verspreiden zaden, bestuiven planten en ruimen de natuur op; ze zijn onmisbaar voor een gezond ecosysteem. Van groot maatschappelijk belang is het beschermen van bedreigde dieren; biodiversiteit zorgt voor een gezond klimaat in Nederland. Voor de bescherming van vogels worden nesten gedetecteerd en geregistreerd. Boeren worden vervolgens geïnformeerd over de aanwezigheid van nesten op hun land zodat ze de nesten niet vernietigen tijdens hun agrarische werkzaamheden. Boeren worden in Nederland gecompenseerd voor de bescherming van nesten waardoor economische belangen samenkomen met het behoud van de natuur. In dit project wordt met behulp van technologische innovatie de samenwerking tussen boeren en natuur- en vogelbescherming verstevigd: drones worden gecombineerd met artificiële intelligentie om in samenwerking met vrijwilligers de monitoring van nesten uit te voeren. Dit helpt de Bond Friese VogelWachten (BFVW) om met het huidige aantal vogelwachters meer nesten te kunnen opsporen, de natuur doordat meer detectie leidt tot hogere broedsucces van vogels, en de boer kan met de drone meer financiële compensatie bemachtigen. Het consortium bestaat uit BFVW, NHL Stenden Lectoraat Computer Vision & Data Science en het drone bedrijf Aeroscan, die gezamenlijk de technische haarbaarheid willen onderzoeken om de business-case te ondersteunen. Met deze technologie kan de BFVW efficiënter en vooral effectiever nesten in kaart brengen. In de toekomst worden de resultaten van dit project breder ingezet door dit consortium. Binnen natuurbehoud en biodiversiteit zijn er veel andere uitdagingen waarvoor de, in dit project ontwikkelde, kennis ingezet kan worden.