Challenges that surveys are facing are increasing data collection costs and declining budgets. During the past years, many surveys at Statistics Netherlands were redesigned to reduce costs and to increase or maintain response rates. From 2018 onwards, adaptive survey design has been applied in several social surveys to produce more accurate statistics within the same budget. In previous years, research has been done into the effect on quality and costs of reducing the use of interviewers in mixed-mode surveys starting with internet observation, followed by telephone or face-to-face observation of internet nonrespondents. Reducing follow-ups can be done in different ways. By using stratified selection of people eligible for follow-up, nonresponse bias may be reduced. The main decisions to be made are how to divide the population into strata and how to compute the allocation probabilities for face-to-face and telephone observation in the different strata. Currently, adaptive survey design is an option in redesigns of social surveys at Statistics Netherlands. In 2018 it has been implemented in the Health Survey and the Public Opinion Survey, in 2019 in the Life Style Monitor and the Leisure Omnibus, in 2021 in the Labour Force Survey, and in 2022 it is planned for the Social Coherence Survey. This paper elaborates on the development of the adaptive survey design for the Labour Force Survey. Attention is paid to the survey design, in particular the sampling design, the data collection constraints, the choice of the strata for the adaptive design, the calculation of follow-up fractions by mode of observation and stratum, the practical implementation of the adaptive design, and the six-month parallel design with corresponding response results.
DOCUMENT

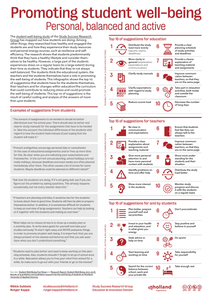
The student well-being study of the Study Success Research Group has mapped out how students are doing. Among other things, they researched how healthy and engaged the students are and how they experience their study resources and personal energy sources, such as resilience and selfefficiency. The research shows that students predominantly think that they have a healthy lifestyle and consider themselves to be healthy. However, a large part of the students experiences stress on a regular basis (to a large extent) during their time as students. This infographic shows the top 10 of suggestions that students have for the students themselves, their teachers and for changes within education/the curriculum that could contribute to reducing stress and could promote the well-being of students.
DOCUMENT
Most higher education alumni work in professional fields, making higher education responsible for the provision of high-quality professionalism throughout society. However, higher education does not yet fulfil its role as a provider of methodologies for the renewal of professionalism. In this lecture, Didi Griffioen outlines the characteristics of professionalism, asserting that current methodologies for the continuous renewal of different elements of professionalism are lacking. By positioning itself as provider of these methodologies, higher education can play a more relevant role in society while also contributing to its own professional renewal and innovativeness.
DOCUMENT

CRISPR/Cas genome engineering unleashed a scientific revolution, but entails socio-ethical dilemmas as genetic changes might affect evolution and objections exist against genetically modified organisms. CRISPR-mediated epigenetic editing offers an alternative to reprogram gene functioning long-term, without changing the genetic sequence. Although preclinical studies indicate effective gene expression modulation, long-term effects are unpredictable. This limited understanding of epigenetics and transcription dynamics hampers straightforward applications and prevents full exploitation of epigenetic editing in biotechnological and health/medical applications.Epi-Guide-Edit will analyse existing and newly-generated screening data to predict long-term responsiveness to epigenetic editing (cancer cells, plant protoplasts). Robust rules to achieve long-term epigenetic reprogramming will be distilled based on i) responsiveness to various epigenetic effector domains targeting selected genes, ii) (epi)genetic/chromatin composition before/after editing, and iii) transcription dynamics. Sustained reprogramming will be examined in complex systems (2/3D fibroblast/immune/cancer co-cultures; tomato plants), providing insights for improving tumor/immune responses, skin care or crop breeding. The iterative optimisations of Epi-Guide-Edit rules to non-genetically reprogram eventually any gene of interest will enable exploitation of gene regulation in diverse biological models addressing major societal challenges.The optimally balanced consortium of (applied) universities, ethical and industrial experts facilitates timely socioeconomic impact. Specifically, the developed knowledge/tools will be shared with a wide-spectrum of students/teachers ensuring training of next-generation professionals. Epi-Guide-Edit will thus result in widely applicable effective epigenetic editing tools, whilst training next-generation scientists, and guiding public acceptance.
In the last decade, the concept on interactions between humans, animals and their environment has drastically changed, endorsed by the One Health approach that recognizes that health of humans and animals are inextricably linked. Consideration of welfare of livestock has increased accordingly and with it, attention into the possibilities to improve livestock health via natural, more balanced nutrition is expanding. Central to effects of healthy nutrition is an optimal gastrointestinal condition which entails a well-balanced functional local immune system leading to a resilient state of well-being. This project proposal, GITools, aims to establish a toolbox of in vitro assays to screen new feed ingredients for beneficial effects on gastrointestinal health and animal well-being. GITools will focus on pig and chicken as important livestock species present in high quantities and living in close proximity to humans. GITools builds on intestinal models (intestinal cell lines and stem cell-derived organoids), biomarker analysis, and in vitro enzymatic and microbial digestion models of feed constituents. The concept of GITools originated from various individual contacts and projects with industry partners that produce animal feed (additives) or veterinary medicines. Within these companies, an urgent need exists for straightforward, well-characterized and standardized in vitro methods that provide results translatable to the in vivo situation. This to replace testing of new feed concepts in live animal. We will examine in vitro methods for their applicability with feed ingredients selected based on the availability of data from (previous) in vivo studies. These model compounds will include long and short chain fatty acids, oligosaccharides and herbal-derived components. GITools will deliver insights on the role of intestinal processes (e.g. dietary hormone production, growth of epithelial cells, barrier function and innate immune responses) in health and well-being of livestock animals and improve the efficiency of testing new feed products.