Background: To avoid overexertion in critically ill patients, information on the physical demand, i.e., metabolic load, of daily care and active exercises is warranted. Objective: The objective of this study was toassess the metabolic load during morning care activities and active bed exercises in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients. Methods: This study incorporated an explorative observational study executed in a university hospital intensive care unit. Oxygen consumption (VO2) was measured in mechanically ventilated (≥48 h) critically ill patients during rest, routine morning care, and active bed exercises. We aimed to describe and compare VO2 in terms of absolute VO2 (mL) defined as the VO2 attributable to the activity and relative VO2 in mL per kilogram bodyweight, per minute (mL/kg/min). Additional outcomes achieved during the activity were perceived exertion, respiratory variables, and the highest VO2 values. Changes in VO2 and activity duration were tested using paired tests. Results: Twenty-one patients were included with a mean (standard deviation) age of 59 y (12). Median (interquartile range [IQR]) durations of morning care and active bed exercises were 26 min (21–29) and 7 min (5–12), respectively. Absolute VO2 of morning care was significantly higher than that of active bed exercises (p = 0,009). Median (IQR) relative VO2 was 2.9 (2.6–3.8) mL/kg/min during rest; 3.1 (2.8–3.7) mL/kg/min during morning care; and 3.2 (2.7–4) mL/kg/min during active bed exercises. The highest VO2 value was 4.9 (4.2–5.7) mL/kg/min during morning care and 3.7 (3.2–5.3) mL/kg/min during active bed exercises. Median (IQR) perceived exertion on the 6–20 Borg scale was 12 (10.3–14.5) during morning care (n = 8) and 13.5 (11–15) during active bed exercises (n = 6). Conclusion: Absolute VO2 in mechanically ventilated patients may be higher during morning care than during active bed exercises due to the longer duration of the activity. Intensive care unit clinicians should be aware that daily-care activities may cause intervals of high metabolic load and high ratings of perceived exertion.
DOCUMENT

Purpose: The increasing number of cancer survivors has heightened demands on hospital-based follow-up care resources. To address this, involving general practitioners (GPs) in oncological follow-up is proposed. This study explores secondary care providers’ views on integrating GPs into follow-up care for curatively treated breast and colorectal cancer survivors. Methods: A qualitative exploratory study was conducted using semi-structured interviews with Dutch medical specialists and nurse practitioners. Interviews were recorded, transcribed verbatim, and analyzed using thematic analysis by two independent researchers. Results: Fifteen medical specialists and nine nurse practitioners participated. They identified barriers such as re-referral delays, inexperience to perform structured follow-up, and worries about the lack of oncological knowledge among GPs. Benefits included the GPs’ accessibility and their contextual knowledge. For future organization, they emphasized the need for hospital logistics changes, formal GP training, sufficient case-load, proper staffing, remuneration, and time allocation. They suggested that formal GP involvement should initially be implemented for frail older patients and for prevalent cancer types. Conclusions: The interviewed Dutch secondary care providers generally supported formal involvement of primary care in cancer follow-up. A well-organized shared-care model with defined roles and clear coordination, supported by individual patients, was considered essential. This approach requires logistics adaptation, resources, and training for GPs. Implications for cancer survivors: Integrating oncological follow-up into routine primary care through a shared-care model may lead to personalized, effective, and efficient care for survivors because of their long-term relationships with GPs.
DOCUMENT

Through a qualitative examination, the moral evaluations of Dutch care professionals regarding healthcare robots for eldercare in terms of biomedical ethical principles and non-utility are researched. Results showed that care professionals primarily focused on maleficence (potential harm done by the robot), deriving from diminishing human contact. Worries about potential maleficence were more pronounced from intermediate compared to higher educated professionals. However, both groups deemed companion robots more beneficiary than devices that monitor and assist, which were deemed potentially harmful physically and psychologically. The perceived utility was not related to the professionals' moral stances, countering prevailing views. Increasing patient's autonomy by applying robot care was not part of the discussion and justice as a moral evaluation was rarely mentioned. Awareness of the care professionals' point of view is important for policymakers, educational institutes, and for developers of healthcare robots to tailor designs to the wants of older adults along with the needs of the much-undervalued eldercare professionals.
DOCUMENT

Wat dragen creatieve onderzoeksmethodes bij aan vernieuwing binnen de zorg? We onderzoeken dit binnen tien projecten van het Create Health-programma van ZonMw. In deze projecten wordt kennis ontwikkeld over de toegevoegde waarde van creatieve manieren van werken bij e-health innovatie.
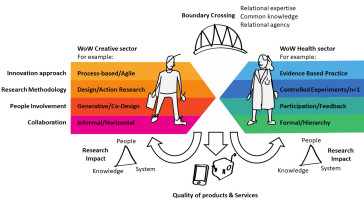
Wat dragen creatieve onderzoeksmethodes bij aan vernieuwing binnen de zorg? We onderzoeken dit binnen tien projecten van het Create Health-programma van ZonMw. In deze projecten wordt kennis ontwikkeld over de toegevoegde waarde van creatieve manieren van werken bij e-health innovatie. Informatie over de onderzoeksresultaten is te vinden op de website: husite.nl/creatieve-onderzoeksmethodes en het artikel: CHIWaWA maakt samenwerking in create-health onderzoek inzichtelijk | Hogeschool Utrecht (hu.nl)Doel Het Create Health programma heeft tot doel om bij te dragen aan maatschappelijke uitdagingen rondom gezond en actief ouder worden. CHIWaWA werkt daarbij toe naar een conceptueel model dat manieren van werken in kaart brengt in create health projecten – gekoppeld aan theorie over boundary crossing en research impact – met betrekking tot projectuitkomsten en kennis-, persoonlijke-, en systeemontwikkeling van betrokken actoren. Resultaten onderzoek Kennis die zowel online als offline te raadplegen is, in een boek, in wetenschappelijke artikelen en op een website. Deze kennis bevat: Inzicht in kansen om impact van e-health innovatie in ‘create health’-samenwerking te vergroten; Projectnarratieven met ‘best practices’ voor interdisciplinaire samenwerking waarbij onderzoekers, creatieve industrie en zorgprofessionals betrokken zijn; Guidelines voor ontwikkelaars van e-health applicaties m.b.t. samenwerking met de creatieve industrie; Guidelines voor beleidsmakers m.b.t. het stimuleren van samenwerking tussen zorg en creatieve industrie en het gebruik van creatieve manieren van werken om onderzoek naar de praktijk te krijgen; Aanpak Vanuit een service-dominant logic perspectief wordt bekeken hoe toegepaste kennis en skills worden gedeeld tussen actoren die betrokken zijn bij de verschillende ‘create health’-projecten, wat de meerwaarde daarvan is en wat actoren van die uitwisseling – als proces – leren. De focus ligt op co-creatie van waarde, die door samenwerking en uitwisseling tot stand komt. Door middel van procesonderzoek wordt er toegewerkt naar bijdragen aan theorieontwikkeling op het gebied van boundary crossing en contribution mapping. Resultaten Eindpublicatie: Create Health: Samenwerking tussen zorg, wetenschap en creatieve industrie (2023) Boek: Create Ways of Working. Insights from ten ehealth Innovation research projects (2022) Website www.creatieveonderzoeksmethodes.nl (2022) Bijdragen aan conferenties en symposia Co-design in de anderhalvemetermaatschappij (whitepaper), Dutch Design Week 2020. Download de presentatieslides. Collaborating in complexity. Strategies for interdisciplinary collaboration n design work, Design4Health conference 2020 Grounding Practices. How researchers ground their work in create-health collaborations for designing e-health solutions, Design4Health conference 2020 Seven ways to foster interdisciplinary collaboration in research involving healthcare and creative research disciplines, DementiaLab conference 2019 Posterpresentatie: Health x Design, DementiaLab conference 2019 Meer informatie over het Create Health programma Het ZonMw programma Create Health heeft als doel om bij te dragen aan de maatschappelijke uitdaging rondom gezond en actief ouder worden. Binnen het programma worden activiteiten uitgezet waarbij de samenwerking tussen de creatieve industrie en zorg en welzijn voorop staat. Het gaat hierbij om publiek-private samenwerking (PPS).
Youth care is under increasing pressure, with rising demand, longer waiting lists, and growing staff shortages. In the Netherlands, one in seven children and adolescents is currently receiving youth care. At the same time, professionals face high workloads, burnout risks, and significant administrative burdens. This combination threatens both the accessibility and quality of care, leading to escalating problems for young people and families. Artificial intelligence (AI) offers promising opportunities to relieve these pressures by supporting professionals in their daily work. However, many AI initiatives in youth care fail to move beyond pilot stages, due to barriers such as lack of user acceptance, ethical concerns, limited professional ownership, and insufficient integration into daily practice. Empirical research on how AI can be responsibly and sustainably embedded in youth care is still scarce. This PD project aims to develop practice-based insights and strategies that strengthen the acceptance and long-term adoption of AI in youth care, in ways that support professional practice and contribute to appropriate care. The focus lies not on the technology itself, but on how professionals can work with AI within complex, high-pressure contexts. The research follows a cyclical, participatory approach, combining three complementary implementation frameworks: the Implementation Guide (Kaptein), the CFIR model (Damschroder), and the NASSS-CAT framework (Greenhalgh). Three case studies serve as core learning environments: (1) a speech-to-text AI tool to support clinical documentation, (2) Microsoft Copilot 365 for organization-wide adoption in support teams, and (3) an AI chatbot for parents in high-conflict divorces. Throughout the project, professionals, clients, ethical experts, and organizational stakeholders collaborate to explore the practical, ethical, and organizational conditions under which AI can responsibly strengthen youth care services.