This text is based on the publication: Wolff, R. & M. de Jong (2018), Doceren voor een inclusieve klas. Een literatuurstudie ter voorbereiding op docenttrainingen in het hoger (beroeps)onderwijs. (Teaching for an inclusive class. A literature study as preparatory input for teacher trainings in higher (vocational) education) Diemen/Rotterdam: Inholland/Risbo
DOCUMENT

The inclusive education debate is often framed as a choice between outmoded special schools and progressive inclusive general education schools. However, the rhetoric of ‘choice’ hides what is in reality a context of restricted resources, both in general education and in special congregated settings. We interview three deaf-parented families with a total of six deaf children enrolled in different educational settings in Belgium. We explore the educational choices parents made for their children and how these choices are influenced (1) by their own knowledge of and lived experience with the educational choices available and (2) actually existing resources. Our study shows a clear contrast between the capital parents bring to their children’s educational experiences and the choices available. Parents want to send their children to congregated settings to give them an education in sign language but are hindered from doing so because of the schools’ lack of adherence to educational standards. Instead they are pushed into a general education system that tasks their time and energy, as well as their child’s bodies. The paucity of options for these parents calls for a rethinking of the parameters of the inclusive education debate, moving beyond placement to a holistic focus on deaf children’s linguistic, educational, and social development.
DOCUMENT
Inclusief onderwijs staat hoog op de agenda van De Haagse Hogeschool. Sinds januari 2021 is Naomi van Stapele lector Inclusive Education bij het kenniscentrum Global & Inclusive Learning. In deze intreerede van september 2022 wordt o.a. ingegaan op onzekerheid, de drie leidende beginselen van inclusief onderwijs, de ethische politiek van inclusiviteit, etc.
DOCUMENT

In the Netherlands and the USA, the assessment process is changing for children who present learning and behavioural challenges in school. Evaluations for eligibility determinations and support planning are shifting along with disability models and tensions over the provision of inclusive schooling. Legislative edicts influence the assessment process differently in these two countries while both nations seem to be headed in a similar direction. This paper relates evolving disability models to the changing assessment process in each country and proposes that a solution-focused perspective offers an assessment concept which supports the goal of inclusive education. Specifically discussed are the implications of a solution-focused approach on the identification of disability, the assessment of special educational needs, individualised support planning and the essential cooperation within evolving schools as well as the environment beyond.
DOCUMENT
The European Manifesto for Inclusive Learning is an initiative of the University of Florence to promote adult education for migrants and refugees. The program seeks to provide “a concrete tool for adult educators to promote adult learning in their local context”. In order to achieve this goal, eight European Union partners in different EU countries collaborated intensively for 1 ½ year to exchange experiences, expand opportunities and to seek to promote a more coordinated and integrated approach. Each partner collected case studies of good practices using a common tool for collecting data. The results of the Dutch partner, The Hague University of Applied Sciences are presented here. Seven cases have been studied with very different, mainly informal ways of mutual learning in the Netherlands. First the Manifesto is described in more detail. This is followed by a sketch of refugee flows to the Netherlands and the Dutch asylum system. After these chapters, the different cases are presented, followed by a conclusion and recommendations based on the Dutch good practices.
DOCUMENT

Worldwide, pupils with migrant backgrounds do not participate in school STEM subjects as successfully as their peers. Migrant pupils’ subject-specific language proficiency lags behind, which hinders participation and learning. Primary teachers experience difficulty in teaching STEM as well as promoting required language development. This study investigates how a professional development program (PDP) focusing on inclusive STEM teaching can promote teacher learning of language-promoting strategies (promoting interaction, scaffolding language and using multilingual resources). Participants were five case study teachers in multilingual schools in the Netherlands (N = 2), Sweden (N = 1) and Norway (N = 2), who taught in primary classrooms with migrant pupils. The PDP focused on three STEM units (sound, maintenance, plant growth) and language-promoting strategies. To trace teachers’ learning, three interviews were conducted with each of the five teachers (one after each unit). The teachers also filled in digital logs (one after each unit). The interviews showed positive changes in teachers’ awareness, beliefs and attitudes towards language-supporting strategies. However, changes in practice and intentions for practice were reported to a lesser extent. This study shows that a PDP can be an effective starting point for teacher learning regarding inclusive STEM teaching. It also illuminates possible enablers (e.g., fostering language awareness) or hinderers (e.g., teachers’ limited STEM knowledge) to be considered in future PDP design.
LINK
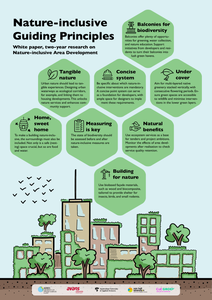
Urban nature enhancement is a theme that needs to be considered across different scales. From pocket parks and façade-greening to urban green infrastructure, biodiversity thrives best through connectivity.In the SIA-project, Nature-inclusive Area Development, four universities of applied sciences - Aeres University of Applied Sciences, Avans University of Applied Sciences, Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences, and Van Hall Larenstein University of AppliedSciences- researched three levels of area development to accelerate the transition to nature-inclusive area development. The study consisted of three case studies: Waarder Railway Zone (building), Knowledge Mile Park (KMP - street - Amsterdam), and AlmereCentre-Pampus (area).
DOCUMENT
The purpose of this contribution is twofold. On the one hand we present an overview of recent international developments on inclusive education since the Salamanca Declaration (UNESCO, 1994). We also present the more general challenges and dilemmas this new approach generated, along with a series of promising approaches that have been developed internationally. We will argue – in agreement with many others – that inclusive education requires taking distance from a (dominant) medical-deficit approach in favour of a citizenship approach, which is connected to the Human Rights discussion. Finally, we will argue that the foregoing also suggests an alternative approach towards research in education: a more participative and reflective approach. We then present some examples of research developed and applied by the two authors in which people with disabilities and the professionals working with them were not considered ‘objects of research’, but were research partners throughout the process. The main working principles of this approach will be described and we will discuss some salient results of it.
DOCUMENT
This paper examines the Erasmus Mundus Special Educational Needs (EMSEN) programme experience and the ways in which it influenced the authors' perception of reflection and research involving inclusive education. The authors argue that incorporating reflective practice and research into an international Master's programme holds promise for further inclusive educational practices for students with disabilities globally. The potential impact of collaborative projects that link researchers from highly diverse contexts is explored. The process of reflection in collaborative research enhances the researchers' ability to see their own context through new perspective. The authors describe how the EMSEN programme builds capacity for international research collaborations from the point of view of student, visiting scholar and programme convener. The authors, each from their own role, cultural background and perspective, reflect on several problems encountered in the EM year, how they tried to cope with these and recount how the challenges build capacity for future collaboration.
DOCUMENT
Large groups in society lack the necessary skills to be sufficiently self-reliant and are in need of personal assistance. These groups could be supported by information and information technology (ICT), but only if this technology is designed to fit their (cognitive) abilities. Inclusive design theory and methods have already been developed in research contexts, but there is still a gap between theory and practice. There is a need for a practical aid, that helps to create awareness of inclusive design among ICT developers, and offers easy-to-use information and tools to actually apply the methods for diverse target groups. This paper describes the first steps taken towards an inclusive design toolbox for developing ICT applications that offer cognitive support for selfreliance. Dutch ICT companies were interviewed and participated in a co-design workshop, leading to a number of initial needs, user requirements, and an on-line community, that form input for further development of the toolbox.
DOCUMENT
