Een internationale ervaring vergroot het perspectief op sociaal werk. Nelleke Nijhuis ervoer dit tijdens haar vele reizen naar Kenia. Dit heeft haar zo geïnspireerd, dat ze dagelijks haar buitenlandervaringen meeneemt in haar werk in Nederland. In dit artikel vertelt ze over haar werkwijze en benoemt de opgedane kennis en ervaringen die ze toepast in de door haar ontworpen methodiek ‘My Drive in Life’.
DOCUMENT

Obesity, especially morbid obesity, is a major health problem with considerable impact on physical, mental and social quality of life. Assessment of quality of life is considered crucial to understand and evaluate the consequences of obesity. However, the heterogeneity of the quality of life concept makes it difficult to compare and value studies on quality of life. Both generic -applying to any disease- and obesity specific quality of life instruments can be used as assessment instruments in obesity. Generic instruments have the advantage that they can be used to compare the quality of life consequences of divergent diseases, whereas the major advantage of obesity specific instruments is that these are more sensitive to changes in obesity. Obesity has major consequences for quality of life, as a result of co-morbidities of obesity, weight stigmatization, and other less frequently ventilated problems. Bariatric surgery has been proven to lead to significant weight loss and improvement of quality of life. Instruments differ in the suitability to assess quality of life after surgery and weight loss, and they differ in the domains of quality of life that are tapped by the instruments. Besides obesity, also personal and psychosocial variables influence quality of life and affect the outcome of surgery. Obesity, even after substantial weight loss by gastric bypass surgery, is a chronic disease requiring life long consideration, in order to attain long standing quality of life improvement.
DOCUMENT
Obesity, especially morbid obesity, is a major health problem with considerable impact on physical, mental and social quality of life. Assessment of quality of life is considered crucial to understand and evaluate the consequences of obesity. Obesity has major consequences for quality of life, e.g., as a result of co-morbidities of obesity and weight stigmatization.Bariatric surgery has been proven to lead to significant weight loss and improvement of quality of life. Besides obesity, also personal and psychosocial variables influence quality of life and affect the outcome of surgery. Moreover, obesity, even after substantial weight loss by gastric bypass surgery, is a chronic disease requiring life long consideration, in order to sustain long standing quality of life improvement.
DOCUMENT
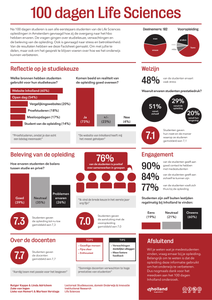
Na 100 dagen studeren is aan alle eerstejaars studenten van de Life Sciences opleidingen in Amsterdam gevraagd hoe zij de overgang naar het hbo hebben ervaren. De vragen gingen over studiekeuze, verwachtingen en de beleving van de opleiding. Ook is gevraagd naar stress en betrokkenheid. Van de resultaten hebben we deze factsheet gemaakt.
DOCUMENT
Abstract Purpose To determine the predictive value of quality of life for mortality at the domain and item levels. Methods This longitudinal study was carried out in a sample of 479 Dutch people aged 75 years or older living independently, using a follow-up of 7 years. Participants completed a self-report questionnaire. Quality of life was assessed with the WHOQOL-BREF, including four domains: physical health, psychological, social relationships, and environment. The municipality of Roosendaal (a town in the Netherlands) indicated the dates of death of the individuals. Results Based on mean, all quality of life domains predicted mortality adjusted for gender, age, marital status, education, and income. The hazard ratios ranged from 0.811 (psychological) to 0.933 (social relationships). The areas under the curve (AUCs) of the four domains were 0.730 (physical health), 0.723 (psychological), 0.693 (social relationships), and 0.700 (environment). In all quality of life domains, at least one item predicted mortality (adjusted). Conclusion Our study showed that all four quality of life domains belonging to the WHOQOL-BREF predict mortality in a sample of Dutch community-dwelling older people using a follow-up period of 7 years. Two AUCs were above threshold (psychological, physical health). The findings offer health care and welfare professionals evidence for conducting interventions to reduce the risk of premature death.
DOCUMENT

Introduction Many health care interventions have been developed that aim to improve or maintain the quality of life for frail elderly. A clear overview of these health care interventions for frail elderly and their effects on quality of life is missing. Purpose To provide a systematic overview of the effect of health care interventions on quality of life of frail elderly. Methods A systematic search was conducted in Embase, Medline (OvidSP), Cochrane Central, Cinahl, PsycInfo and Web of Science, up to and including November 2017. Studies describing health care interventions for frail elderly were included if the effect of the intervention on quality of life was described. The effects of the interventions on quality of life were described in an overview of the included studies. Results In total 4,853 potentially relevant articles were screened for relevance, of which 19 intervention studies met the inclusion criteria. The studies were very heterogeneous in the design: measurement of frailty, health care intervention and outcome measurement differ. Health care interventions described were: multidisciplinary treatment, exercise programs, testosterone gel, nurse home visits and acupuncture. Seven of the nineteen intervention studies, describing different health care interventions, reported a statistically significant effect on subdomains of quality of life, two studies reported a statistically significant effect of the intervention on the overall quality of life score. Ten studies reported no statistically significant difference between the intervention and control groups. Conclusion Reported effects of health care interventions on frail elderly persons’ quality of life are inconsistent, with most of the studies reporting no differences between the intervention and control groups. As the number of frail elderly persons in the population will continue to grow, it will be important to continue the search for effective health care interventions. Alignment of studies in design and outcome measurements is needed.
MULTIFILE

This paper explores how the concept of life has been used in video games through time. Life is an essential element in different types of action games and several nuances have been used to provide various types of emotions and effects during gameplay. However, the details and patterns have not been extendedly analyzed. Primarily, we survey works regarding the description and formalization of game analysis with emphasis on works in which the concepts have impact in the arguably accepted notion of life. Multiple examples are provided to show different approaches to the concept of life and the impact of such approaches in overall gameplay, namely in the game difficulty and emotions. The examples are then generalized, resulting in a proposal of framework to describe life representation in games. The proposed framework was evaluated in a user study, having participants with gaming culture (professionals, academics, and students of game development courses). Each participant was assigned with the task of fitting a preselected set of games within the framework. The results indicate good coverage of the main concepts with satisfactory consistency.
LINK
This paper explores how the concept of life has been used in video games through time. Life is an essential element in different types of action games and several nuances have been used to provide various types of emotions and effects during gameplay. However, the details and patterns have not been extendedly analyzed. Primarily, we survey works regarding the description and formalization of game analysis with emphasis on works in which the concepts have impact in the arguably accepted notion of life. Multiple examples are provided to show different approaches to the concept of life and the impact of such approaches in overall gameplay, namely in the game difficulty and emotions. The examples are then generalized, resulting in a proposal of framework to describe life representation in games. The proposed framework was evaluated in a user study, having participants with gaming culture (professionals, academics, and students of game development courses). Each participant was assigned with the task of fitting a preselected set of games within the framework. The results indicate good coverage of the main concepts with satisfactory consistency.
LINK
This paper explores the construction of self-narratives through a synthesis of two frameworks: Designing Your Life (DYL) and Theory U. Using close reading methodology, it analyzes how these approaches inform personal and professional development. The study highlights three key dimensions: doing (prototyping life choices), believing (leveraging intuition), and empowering (considering broader impacts). While DYL emphasizes rapid experimentation in career design, Theory U focuses on systemic change through "presencing." The integration of these perspectives reveals that self-narratives are intricately linked with social systems and future generations. This synthesis advances the discourse on life design by encouraging researchers to consider the role of the Self in historical and future-oriented contexts and by prompting exploration of intuition and narrative co-creation in fields like education and organizational change. The paper concludes that conscious narrative shaping, informed by both action and reflection, is crucial for meaningful personal development in an interconnected world.
DOCUMENT
