Objectives: The aim of this study was to determine how diagnosing and coding of malnutrition in an internal medicine ward setting influences potential hospital reimbursement. Methods: Patients admitted to the internal medicine ward of Centro Hospitalar do Médio Ave between April 24 and May 22, 2018 were screened by Nutritional Risk Screening 2002, and patients classified as at “risk for malnutrition” were assessed by the Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment (PG-SGA). For each patient, medical coders simulated coding, taking into account the malnutrition diagnosis by PG-SGA, and compared it with the real coding as retrieved from the medical records. For the coding, the Diagnosis-Related Group and Severity of Illness were determined, allowing the calculation of hospitalization cost (HC) according to Portuguese Ministerial Directive number 207/2017. The increase of HC in this subsample was extrapolated to the number of patients admitted during 2018, to obtain the estimated unreported annual HC. Results: Of the 71% (92/129) participants having malnutrition risk according to Nutritional Risk Screening 2002, 86% were malnourished. Including malnutrition diagnosis in the coding of malnourished patients increased the level of Severity of Illness in 39% of cases and increased HC for this subsample, resulting in €52 000. Extrapolating for the annual HC, total HC reached €1.3 million. Conclusions: Identifying malnourished patients and including this highly prevalent diagnosis in medical records allows malnutrition coding and consequent increase of HC. This can improve the potential hospital reimbursement, which could contribute to the quality of patient care and economic sustainability of hospitals.
DOCUMENT
Background: The Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM) approach to malnutrition diagnosis is based on assessment of three phenotypic (weight loss, low body mass index, and reduced skeletal muscle mass) and two etiologic (reduced food intake/assimilation and disease burden/inflammation) criteria, with diagnosis confirmed by fulfillment of any combination of at least one phenotypic and at least one etiologic criterion. The original GLIM description provided limited guidance regarding assessment of inflammation, and this has been a factor impeding further implementation of the GLIM criteria. We now seek to provide practical guidance for assessment of inflammation. Methods: A GLIM-constituted working group with 36 participants developed consensus-based guidance through a modified Delphi review. A multiround review and revision process served to develop seven guidance statements. Results: The final round of review was highly favorable, with 99% overall “agree” or “strongly agree” responses. The presence of acute or chronic disease, infection, or injury that is usually associated with inflammatory activity may be used to fulfill the GLIM disease burden/inflammation criterion, without the need for laboratory confirmation. However, we recommend that recognition of underlying medical conditions commonly associated with inflammation be supported by C-reactive protein (CRP) measurements when the contribution of inflammatory components is uncertain. Interpretation of CRP requires that consideration be given to the method, reference values, and units (milligrams per deciliter or milligram per liter) for the clinical laboratory that is being used. Conclusion: Confirmation of inflammation should be guided by clinical judgment based on underlying diagnosis or condition, clinical signs, or CRP.
DOCUMENT
Background & aims: The Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM) approach to malnutrition diagnosis is based on assessment of three phenotypic (weight loss, low body mass index, and reduced skeletal muscle mass) and two etiologic (reduced food intake/assimilation and disease burden/inflammation) criteria, with diagnosis confirmed by fulfillment of any combination of at least one phenotypic and at least one etiologic criterion. The original GLIM description provided limited guidance regarding assessment of inflammation and this has been a factor impeding further implementation of the GLIM criteria. We now seek to provide practical guidance for assessment of inflammation in support of the etiologic criterion for inflammation. Methods: A GLIM-constituted working group with 36 participants developed consensus-based guidance through a modified-Delphi review. A multi-round review and revision process served to develop seven guidance statements. Results: The final round of review was highly favorable with 99 % overall “agree” or “strongly agree” responses. The presence of acute or chronic disease, infection or injury that is usually associated with inflammatory activity may be used to fulfill the GLIM disease burden/inflammation criterion, without the need for laboratory confirmation. However, we recommend that recognition of underlying medical conditions commonly associated with inflammation be supported by C-reactive protein (CRP) measurements when the contribution of inflammatory components is uncertain. Interpretation of CRP requires that consideration be given to the method, reference values, and units (mg/dL or mg/L) for the clinical laboratory that is being used. Conclusion: Confirmation of inflammation should be guided by clinical judgement based upon underlying diagnosis or condition, clinical signs, or CRP.
DOCUMENT
Malnutrition is an alarming and ongoing healthcare problem globally. Malnutrition has a negative impact on the individual patient, leading to poorer clinical outcomes and increased mortality, but also poses an economic burden on society. Proper identification and diagnostics are prerequisites for initiation of treatment. In 2019, the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition, a consensus-based global framework to uniformly diagnose malnutrition across populations, healthcare settings, and countries was published. Identifying and treating malnutrition is an interdisciplinary team effort. Nonetheless, the nutrition and dietetics profession is specifically trained for diagnosing and treating nutrition(-related) conditions, and therefore has a key role in the interdisciplinary team in implementing the GLIM framework in clinical practice. For the nutrition and dietetics profession, GLIM offers a great opportunity for moving both the scientific and clinical knowledge of malnutrition management forward. While the GLIM framework has been extensively studied since its launch, various knowledge gaps still remain. For the nutrition and dietetics profession, these knowledge gaps mainly relate to the GLIM implementation process, to the role of GLIM in relation to the nutrition care process, and to treatment strategies for various nutrition-related conditions. In this opinion paper, we aimed to describe the rationale for implementing the GLIM framework in clinical dietetic practice, and propose a research agenda based on knowledge gaps regarding GLIM in relation to nutrition care from a dietetic point of view.
DOCUMENT
Introduction: This study evaluates the course of physical fitness and nutritional status during curative therapy for esophageal cancer, after implementation of a prehabilitation program. Additionally, the impact of baseline physical fitness level and severe postoperative complications on the course of individual patients were explored. Materials and methods: This multicenter, observational cohort study included patients with esophageal cancer following curative treatment. Prehabilitation, consisting of supervised exercise training and nutritional counseling was offered as standard care to patients after neoadjuvant therapy, prior to surgery. Primary outcome measures included change of exercise capacity, hand grip strength, self-reported physical functioning, Body Mass Index, and malnutrition risk from diagnosis to 2–6 months postoperatively. Analyses over time were performed using linear mixed models, and linear mixed regression models to investigate the impact of baseline level and severe postoperative complications. Results: Hundred sixty-eight patients were included (mean age 65.9 ± 8.6 years; 78.0 % male). All parameters (except for malnutrition risk) showed a decline during neoadjuvant therapy (p < .05), an improvement during prehabilitation (p < .005) and a decline postoperatively (p < .001), with a high heterogeneity between patients. Change in the outcomes from baseline to postoperatively was not different for patients with or without a severe complication. Better baseline physical fitness and nutritional status were significantly associated with a greater decline postoperatively (p < .001). Conclusion: This study demonstrates a notable decline during neoadjuvant therapy, that fully recovers during prehabilitation, and a subsequent long lasting decline postoperatively. The heterogeneity in the course of physical fitness and nutritional status underlines the importance of individualized monitoring.
DOCUMENT

Background: Early identification of older cardiac patients at high risk of readmission or mortality facilitates targeted deployment of preventive interventions. In the Netherlands, the frailty tool of the Dutch Safety Management System (DSMS-tool) consists of (the risk of) delirium, falling, functional impairment, and malnutrition and is currently used in all older hospitalised patients. However, its predictive performance in older cardiac patients is unknown. Aim: To estimate the performance of the DSMS-tool alone and combined with other predictors in predicting hospital readmission or mortality within 6 months in acutely hospitalised older cardiac patients. Methods: An individual patient data meta-analysis was performed on 529 acutely hospitalised cardiac patients ≥70 years from four prospective cohorts. Missing values for predictor and outcome variables were multiply imputed. We explored discrimination and calibration of: (1) the DSMS-tool alone; (2) the four components of the DSMS-tool and adding easily obtainable clinical predictors; (3) the four components of the DSMS-tool and more difficult to obtain predictors. Predictors in model 2 and 3 were selected using backward selection using a threshold of p = 0.157. We used shrunk c-statistics, calibration plots, regression slopes and Hosmer-Lemeshow p-values (PHL) to describe predictive performance in terms of discrimination and calibration. Results: The population mean age was 82 years, 52% were males and 51% were admitted for heart failure. DSMS-tool was positive in 45% for delirium, 41% for falling, 37% for functional impairments and 29% for malnutrition. The incidence of hospital readmission or mortality gradually increased from 37 to 60% with increasing DSMS scores. Overall, the DSMS-tool discriminated limited (c-statistic 0.61, 95% 0.56-0.66). The final model included the DSMS-tool, diagnosis at admission and Charlson Comorbidity Index and had a c-statistic of 0.69 (95% 0.63-0.73; PHL was 0.658). Discussion: The DSMS-tool alone has limited capacity to accurately estimate the risk of readmission or mortality in hospitalised older cardiac patients. Adding disease-specific risk factor information to the DSMS-tool resulted in a moderately performing model. To optimise the early identification of older hospitalised cardiac patients at high risk, the combination of geriatric and disease-specific predictors should be further explored.
DOCUMENT

DOCUMENT
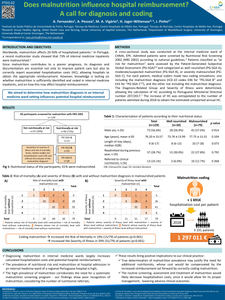
The Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM) created a consensus‐based framework consisting of phenotypic and etiologic criteria to record the occurrence of malnutrition in adults. This is a minimum set of practicable indicators for use in characterizing a patient/client as malnourished, considering the global variations in screening and nutrition assessment, and to be used across different healthcare settings. As with other consensus‐based frameworks for diagnosing disease states, these operational criteria require validation and reliability testing, as they are currently based solely on expert opinion.
DOCUMENT
The Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM) created a consensus‐based framework consisting of phenotypic and etiologic criteria to record the occurrence of malnutrition in adults. This is a minimum set of practicable indicators for use in characterizing a patient/client as malnourished, considering the global variations in screening and nutrition assessment, and to be used across different healthcare settings. As with other consensus‐based frameworks for diagnosing disease states, these operational criteria require validation and reliability testing, as they are currently based solely on expert opinion.
DOCUMENT
Already at diagnosis, head and neck cancer patients are atrisk for malnutrition. Local symptoms such as swallowingproblems are a major cause of malnutrition in thesepatients.1 Additionally, malnutrition may result fromchanges in smell and taste/aversion and loss of appetite.Presence of these systemic symptoms at diagnosis may beindicative for the cachexia syndrome. Therefore, we testedthe hypothesis that head and neck cancer patients to betreated with primary or postoperative (chemo)radiationsuffer from cachexia.
DOCUMENT