This paper discusses two studies - the one in a business context, the other in a university context - carried out with expert educational designers. The studies aimed to determine the priorities experts claim to employ when designing competence-based learning environments. Designers in both contexts agree almost completely on principles they feel are important. Both groups emphasized that one should start a design enterprise from the needs of the learners, instead of the content structure of the learning domain. However, unlike business designers, university designers find it extremely important to consider alternative solutions during the whole design process. University designers also say that they focus more on project plan and desired characteristics of the instructional blueprint whereas business designers report being more client-oriented, stressing the importance of "buying in" the client early in the process.
DOCUMENT

In the Netherlands, palliative care is provided by generalist healthcare professionals (HCPs) if possible and by palliative care specialists if necessary. However, it still needs to be clarifed what specialist expertise entails, what specialized care consists of, and which training or work experience is needed to become a palliative care special‑ist. In addition to generalists and specialists, ‘experts’ in palliative care are recognized within the nursing and medical professions, but it is unclear how these three roles relate. This study aims to explore how HCPs working in palliative care describe themselves in terms of generalist, specialist, and expert and how this self-description is related to their work experience and education. Methods A cross-sectional open online survey with both pre-structured and open-ended questions among HCPs who provide palliative care. Analyses were done using descriptive statistics and by deductive thematic coding of open-ended questions. Results Eight hundred ffty-four HCPs flled out the survey; 74% received additional training, and 79% had more than fve years of working experience in palliative care. Based on working experience, 17% describe themselves as a generalist, 34% as a specialist, and 44% as an expert. Almost three out of four HCPs attributed their level of expertise on both their education and their working experience. Self-described specialists/experts had more working experience in palliative care, often had additional training, attended to more patients with palliative care needs, and were more often physicians as compared to generalists. A deductive analysis of the open questions revealed the similarities and dis‑ tinctions between the roles of a specialist and an expert. Seventy-six percent of the respondents mentioned the impor‑tance of having both specialists and experts and wished more clarity about what defnes a specialist or an expert, how to become one, and when you need them. In practice, both roles were used interchangeably. Competencies for the specialist/expert role consist of consulting, leadership, and understanding the importance of collaboration. Conclusions Although the grounds on which HCPs describe themselves as generalist, specialist, or experts difer, HCPs who describe themselves as specialists or experts mostly do so based on both their post-graduate education and their work experience. HCPs fnd it important to have specialists and experts in palliative care in addition to gen‑eralists and indicate more clarity about (the requirements for) these three roles is needed.
DOCUMENT

Background: A large number of people participate in individual or unorganized sports on a recreational level. Furthermore, many participants drop out because of injury or lowered motivation. Potentially, physical activity–related apps could motivate people during sport participation and help them to follow and maintain a healthy active lifestyle. It remains unclear what the quality of running, cycling, and walking apps is and how it can be assessed. Quality of these apps was defined as having a positive influence on participation in recreational sports. This information will show which features need to be assessed when rating physical activity–related app quality. Objective: The aim of this study was to identify expert perception on which features are important for the effectiveness of physical activity–related apps for participation in individual, recreational sports. Methods: Data were gathered via an expert panel approach using the nominal group technique. Two expert panels were organized to identify and rank app features relevant for sport participation. Experts were researchers or professionals in the field of industrial design and information technology (technology expert panel) and in the field of behavior change, health, and human movement sciences who had affinity with physical activity–related apps (health science expert panel). Of the 24 experts who were approached, 11 (46%) agreed to participate. Each panel session consisted of three consultation rounds. The 10 most important features per expert were collected. We calculated the frequency of the top 10 features and the mean importance score per feature (0-100). The sessions were taped and transcribed verbatim; a thematic analysis was conducted on the qualitative data. Results: In the technology expert panel, applied feedback and feedforward (91.3) and fun (91.3) were found most important (scale 0-100). Together with flexibility and look and feel, these features were mentioned most often (all n=4 [number of experts]; importance scores=41.3 and 43.8, respectively). The experts in the health science expert panels a and b found instructional feedback (95.0), motivating or challenging (95.0), peer rating and use (92.0), motivating feedback (91.3), and monitoring or statistics (91.0) most important. Most often ranked features were monitoring or statistics, motivating feedback, works good technically, tailoring starting point, fun, usability anticipating or context awareness, and privacy (all n=3-4 [number of experts]; importance scores=16.7-95.0). The qualitative analysis resulted in four overarching themes: (1) combination behavior change, technical, and design features needed; (2) extended feedback and tailoring is advised; (3) theoretical or evidence base as standard; and (4) entry requirements related to app use. Conclusions: The results show that a variety of features, including design, technical, and behavior change, are considered important for the effectiveness of physical activity–related apps by experts from different fields of expertise. These insights may assist in the development of an improved app rating scale.
LINK
To stimulate democratic competences through teaching, it is necessary to have an understanding of actions and behaviors that are considered effective in teaching methods. In this study, we investigated these actions and behaviors, referred to as classroom practices, by interviewing 20 expert teachers of democracy in the Netherlands. We identified six relevant practices: meaningful embedding, providing multiple perspectives, thinking about solutions from divergent perspectives, independent information collection and presentation, taking socio-political action, and critical reflection on subject matter. We show how these practices are associated with democratic competences and provide examples of how the practices are implemented in teaching methods.
DOCUMENT

Gaming Horizons is a EU-funded project that explored the role of video games in culture, the economy and education. We engaged with more than 280 stakeholders through interviews, workshops and webinars.
LINK
The EU and national governments rely on expert panels and opinions for their policies (EU, 2003; EU, 2006a; EU, 2006b) on SME ownership transfers. Also entrepreneurs depend on expert opinions and advice. We know from expert studies that expert judgment may lead to confusion and conflicting results. Can we rely on expert opinions in ownership transfers, especially if there are different specialists involved? 71 Dutch SME specialists on ownership transfers (accountants, bankers, business brokers, business consultants) and 10 entrepreneurs were interviewed with open questions. The answers were counted and the averages of different groups of specialists were tested by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s HSD. The results indicate that expert opinions are largely divergent on issues, but become convergent on solutions. Most given solutions by experts are more awareness/information and involving professional advice. Not the accountant, the international most widely used advisor by entrepreneurs in ownership transfers, but the business broker seems best fit to advice. Business brokers are active in more phases of the ownership transfer, are better connected to other specialists and have the most structured working method. We detect serious market failure to provide advice for entrepreneurs on business transfers. More than one specialist is needed, the best suited advisor - the business brokers - are unattainable for most micro firms. To overcome market failure transfer vouchers might connect entrepreneurs better to business brokers. Our results are confined by the sample, being small, select and national
DOCUMENT
Hoe kunnen politieteams meer bezig zijn met het oplossen van veiligheidsproblemen in de wijk? Van nature is de politie vooral geneigd te reageren op incidenten. Maar zij wil ook meer aan de oorzaken van problemen werken, samen met anderen. De wijk operationeel expert (WOE) heeft daarin een cruciale rol. Hoe kun je die rol versterken? Wij deden samen met politieteams in Almere, Amersfoort en Utrecht actieonderzoek hiernaar.
DOCUMENT

This dissertation concerns the adaptive ability by which workers meet new expertise needs throughout their careers. We aimed to increase our understanding of this adaptive ability through a series of four studies building upon the concept of flexpertise (Van der Heijden, 1998, 2000). These studies were designed to advance theorizing, specifically in scholarly research on expertise and expert performance (Ericsson et al., 2006) and sustainable careers (Van der Heijden & De Vos, 2015), and to increase our understanding of how flexpertise may be fostered among workers across expertise domains and working contexts.In this introduction chapter, we outline the key theoretical concepts regarding the flexpertise phenomenon that we will use throughout this dissertation, a description of the knowledge gap in the scholarly literature, and our research focus. This is followed by a summary of this PhD project that outlines the overall research objective, the research questions and research methods that we deployed, as well as an overview of the four flexpertise studies conducted (see Table 1.1). The subsequent chapters include the four (submitted) scientific publications on this matter. We conclude by reflecting on the theoretical, methodological and practical value of our research, and on the limitations of our research approach. We finish with recommendations for future research, ethical considerations on the usage of the flexpertise concept in labor market debates, and a personal reflection on this PhD program.Before explaining the key concept of flexpertise and related core concepts, we first outline what we mean by new expertise needs. These needs shaped the background of the four studies conducted.
DOCUMENT

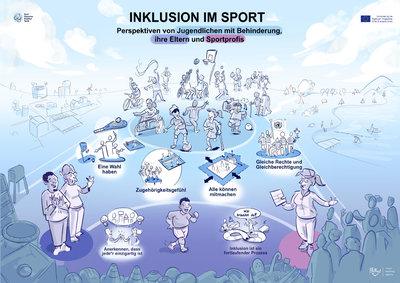
Es war wichtig, die authentischen Ansichten, Wünsche und Empfindungen von Jugendlichen mit Behinderung in Bezug auf Inklusion im Sport zu erhalten. Daher wurden Online-Fokusgruppen mit Kindern und Jugendlichen mit einer Behinderung, ihren Eltern und Expert*innen im Sportbereich in Finnland, Litauen, Portugal und den Niederlanden durchgeführt. Aus diesen Interviews wurden sieben Themen bezüglich Inklusion im Sport identifiziert, die im Folgenden einzeln erläutert werden.
DOCUMENT
The aim of this study was to identify expert perception on which features are important for the effectiveness of physical activity–related apps for participation in individual, recreational sports. This study was part of a research project 'For everyone an app?!'.
DOCUMENT
