Tourism is on course to thwart humanity’s efforts to reach a zero carbon economy because of its high growth rates and carbon intensity. To get out of its carbon predicament, the tourism sector needs professionals with carbon literacy and carbon capability. Providing future professionals in the full spectrum of tourism-related study programmes with the necessary knowledge and skills is essential. This article reports on ten years of experience at a BSc tourism programme with a carbon footprint exercise in which students calculate the carbon footprint of their latest holiday, compare their results with others and reflect on options to reduce emissions. Before they start, the students are provided with a handout with emission factors, a brief introduction and a sample calculation. The carbon footprints usually differ by a factor of 20 to 30 between the highest and lowest. Distance, transport mode and length of stay are almost automatically identified as the main causes, and as the main keys for drastically reducing emissions. The link to the students’ own experience makes the exercise effective, the group comparison makes it fun. As the exercise requires no prior knowledge and is suitable for almost any group size, it can be integrated into almost any tourism-related study programme.
DOCUMENT

This study, part of an R&D project with Dutch tour operators, assessed Dutch consumer preferences towards a carbon label for holiday trips. A general survey (n = 504) assessed the perceived importance of a CO 2 label to consumers. To determine the preferred design, two focus groups (n = 15) followed by a panel study (n = 1246) were performed. Finally, a pilot study (n = 100) assessed potential effects of the label on attitude and booking intention. The general survey's results indicate that a carbon label could impact on the travel choice of some Dutch travellers, when label information is explicit, understandable and simply designed. The focus groups in combination with the panel study showed that Dutch consumers prefer a recognisable carbon label, similar to the EU energy label. The pilot study revealed that consumers' attitudes increased significantly, but that intention to book was not significantly affected for the group that was shown the carbon label. These findings contribute to understanding consumer attitudes towards tourism eco and carbon labels, and their content and design. Implementation of a carbon label for tour packages still requires a number of barriers to be resolved. Sustainability remains a low priority during holiday decision-making.
LINK
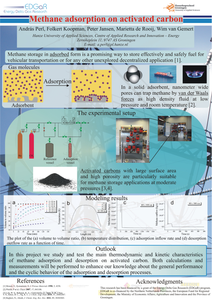
This report presents the experimental and numerical work carried out by ECN and Hanze University of Applied Sciences on methane sorption on activated carbon, as part of their activities within the EDGaR Energy Storage project. Eleven different activated carbon types were tested. It was found that MaxSorb MSC-30 offered the highest methane mass storage density (m/m ratio). However, due to the low density of the MaxSorb MSC-30 activated carbon, the highest volumetric methane storage density (V/V ratio) was found for Brightblack. An increase of the packing density and heat conductivity significantly improves the V/V ratio and shortens the time needed to reach thermal equilibrium. In the case of the Brightblack activated carbon, a total V/V ratio of 112 was found at 12 oC and 40 bar, implying an effective storage density that is 3 times higher than for compressed methane. During the adsorption of methane on activated carbon, sorption heat is released and the temperature of the bed is increased, which negatively affects the effective V/V ratio. Temperature rises up to 70 oC were experimentally observed at higher methane inflow rates. For MaxSorb MSC-30 a temperature rise of 25 oC reduced the effective V/V ratio by about 20 %. The temperature rise of the Brightblack bed caused relatively smaller reductions in the volumetric storage density. Calculations with the validated numerical models indicated an even higher temperature increase for the full scale methane storage, reaching bed temperatures up to 137-150 oC in the case of the MaxSorb MSC-30 activated carbon. At this temperature range, the models indicate a V/V ratio fall down to 46. This performance is similar to the one offered by direct methane compression to 40 bar, and is much lower than the V/V ratio of ~ 100 that was found both experimentally and by calculations for the lab scale reactor performance. The calculations showed, that the low bed permeability can limit the gas flow during adsorption and desorption. A high reactor diameter can countervail the effect of permeability, but the higher dimensions impede the heat dissipation and thus decrease the storage efficiency. Efficient temperature control and management are very important to effectively make use of the methane storage capacity through adsorption.
DOCUMENT
Methane storage in adsorbed form is a promising way to effectively and safely store fuel for vehicular transportation or for any other potential application. In a solid adsorbent, nanometer wide pores can trap methane by van der Waals forces as high density fluid at low pressure and room temperature. This provides the suitable technology to replace bulky and expensive cylindrical compressed natural gas tanks. Activated carbons with large surface area and high porosity are particularly suitable for methane storage applications at moderate pressures. We study and test the main thermodynamic and kinetic characteristics of methane adsorption and desorption on activated carbon.
DOCUMENT
Food production and consumption have a range of sustainability implications, including their contribution to global emissions of greenhouse gases (GHGs). As some foodstuffs entail higher GHG emissions than others, managing their use in tourism-related contexts could make a significant contribution to climate change mitigation. This article reviews the carbon intensity of selected foods and discusses how foodservice providers could adapt their practices. It shows that even though food management could substantially reduce the GHG emissions of foodservice providers, its application is currently hampered by the complexity of food production chains and a lack of dependable data on the GHG intensity of foodstuffs. Nevertheless, it is possible to make a number of recommendations in respect of how foodservice providers can better purchase, prepare and present foods. Further research is now needed to refine and extend our understanding of the contribution that food management can make to reducing tourism's carbon 'foodprint'.
LINK
In the high-tech mechatronics world, aluminum and steel are well known materials, while carbon fiber is often neglected. In the RAAK project 'Composites in Mechatronics', the use of carbon fiber composites in mechatronics is investigated.
DOCUMENT

Contrary to most sectors, to date the tourism and aviation industries have not managed to level off greenhouse gas emissions. Moreover, effective mitigation through technological innovation or structural and behavioural change cannot be expected shortly. Airlines and tourism companies appear to use carbon offsetting as a last resort. However, offsetting is generally acknowledged as a second-best solution for mitigating emissions, after reducing energy use. This paper seeks to determine the mitigation potential of voluntary carbon offsetting by comparing public and industry awareness of climate change and aviation emissions, and attitudes to various mitigation measures with relevant online communication by 64 offset providers. Methods were a literature review and online content analyses. Overall, the gaps that were identified between awareness, attitude and actual behaviour are not bridged by provider communication. From this perspective, the mitigation potential of voluntary carbon offsetting for achieving reductions of tourism transport emissions is estimated as low. The same conclusion is reached by comparing carbon dioxide volumes of flight offsets with actual air travel emissions. Current sales of flight offsets compensate less than 1% of all aviation emissions.
MULTIFILE
In this article, we review the recent progress that has been made in the field of Lewis-acid catalysis of carbon carbon-bond-forming reactions in aqueous solution. Since water hampers the hard hard interactions between the catalyst and the reactant, it often complicates catalysis. However, once coordination has taken place, water can have beneficial effects on rates and selectivities of Lewis acid catalysed Diels Alder reactions, aldol reactions, allylation reactions, Barbier and Mannich type reactions as well as Michael additions.
DOCUMENT
Global leaders agree on the need to substantially decarbonize the global economy by 2050. This paper compares potential costs associated with different policy pathways to achieve tourism sector emission reduction ambitions (−50% by 2035) and transform the sector to be part of the mid-century decarbonized economy (−70% by 2050). Investment in emissions abatement within the tourism sector, combined with strategic external carbon offsets, was found to be approximately 5% more cost effective over the period 2015–2050 than exclusive reliance on offsetting. The cost to achieve the −50% target through abatement and strategic offsetting, while significant, represents less than 0.1% of the estimated global tourism economy in 2020 and 3.6% in 2050. Distributed equally among all tourists (international and domestic), the cost of a low-carbon tourism sector is estimated at US$11 per trip, equivalent to many current travel fees or taxes. Exclusive reliance on offsetting would expose the sector to extensive and continued carbon liability costs beyond mid-century and could be perceived as climate inaction, increasing reputational risks and the potential for less efficient regulatory interventions that could hinder sustainable tourism development. Effective tourism sector leadership is needed to develop a strategic tourism policy framework and emission measurement and reporting system.
LINK
The present study deals with the numerical modelling of hybridlaminated composites, which can be proved especially useful in theengineering and maintenance of advanced aerospace primary structures. Thelamina is comprised of continuous carbon fibers, thermosetting epoxypolymer matrix, as well as carbon nanostructures, such as graphene orcarbon nanotubes, inclusions. Halpin-Tsai equations combined with resultsobtained from nanomechanical analysis are employed in order to evaluatethe elastic properties of the carbon nanostructure/polymer matrix. Then, theobtained elastic properties of the hybrid matrix are used to calculate theorthotropic macro-mechanical properties of the unidirectional compositelamina. A hybrid composite plate is modelled as a 2D structure via theutilization of 4-node, quadrilateral, stress/displacement shell finite elementswith reduced integration formulation. The convergence and analysisaccuracy are tested. The mechanical performance of the hybrid compositesis investigated by considering specific configurations and applyingappropriate loading and boundary conditions. The results are compared withthe corresponding ones found in the open literature, where it is possible.
DOCUMENT
