Poster presented at EFYE 2018. Strengthening the wellbeing of students is an increasingly important approach of the development of students’ social, emotional and academic skills. Personal wellbeing motivates, among other things, students to learn and increases academic involvement and performance accordingly (Noble et al., 2008). According to the Centre for Education of Statistics and Evaluation (CESE, 2015) the educational welfare of students is also important for another reason; the recognition that teaching is not just about achieving academic performance, but also about the welfare of the student as a whole (intellectual, physical, social, emotional, moral and spiritual). Recent studies indicate that more and more students suffer from (mental) health problems (LSvB 2013, 2017; Schaufeli et al., 2002). The aim of the Student Wellbeing Project at Inholland University of Applied Sciences is to 1) investigate the state of student wellbeing in Dutch higher education and investigate the factors that influence wellbeing, 2) explore and offer best practices to improve student wellbeing (curative and preventive) 3) establish a strong (international) partnership and collaborate to improve student wellbeing.
DOCUMENT

Een van de meest populaire modellen voor onderzoek naar welzijn, stress en bevlogenheid van medewerkers is het Job Demands-Resources model (JD-R model). Voor onderzoek naar het welzijn van studenten heeft het lectoraat Studiesucces het Student Wellbeing model ontwikkeld, een model gebaseerd op het JD-R model. Het Student Wellbeing model beschrijft net als het JD-R model een motivatieproces en een uitputtingsproces, maar dan van studenten. Het model veronderstelt dat de balans tussen positieve (energiebronnen) en negatieve (stressoren) kenmerken van ‘het student zijn/de studententijd’ invloed heeft op het welzijn van studenten en o.a. de studieprestaties kan beïnvloeden.
DOCUMENT

At the beginning of May 2020 all Inholland-students received an invitation to participate in a large international study on the corona crisis impact on student life and studies. This poster, presented by the Study Success Research Group, covers relevant results divided in four themes. These themes are student wellbeing, student engagement, satisfaction and the coronavirus. To determine student wellbeing we asked students about their feelings and contacts. Student engagement is phrased in time allocation and engagement. We also wanted to find out how satisfied students were with things like ICT facilities, quality of education and provision of information. Of course we asked students about (not) having corona and adhering to the measures.
DOCUMENT

How are the students of Inholland University of Applied Sciences doing? How do students assess their health and how engaged are they? What are the biggest stressors during their time as a student and what stress reactions do they experience? How resilient and optimistic are the students, and from whom do they get the necessary support? Based on the Student WellBeing Model, this fact sheet shows the most important results of the Student Well-Being Study 2017–2018. The questionnaire was completed by students in the classroom (n=407).
DOCUMENT

The corona pandemic has forced higher education (HE) institutes to transition to online learning, with subsequent implications for student wellbeing. Aims: This study explored influences on student wellbeing throughout the first wave of the corona crisis in the Netherlands by testing serial mediation models of the relationships between perceived academic stress, depression, resilience, and HE support.
MULTIFILE

Dit onderzoek wordt uitgevoerd binnen de onderzoekslijn Studentenwelzijn van het lectoraat Studiesucces. Onderzoek op het gebied van studentenwelzijn in Nederland is nog beperkt. Een van de doelen van de onderzoekslijn is daarom een bijdrage te leveren aan (praktijkgerichte) kennis over het welzijn van studenten. Dit onderzoek heeft als doel daar aan bij te dragen door 1) de stresservaring van studenten binnen Hogeschool Inholland te onderzoeken, 2) in kaart te brengen wat studenten helpt om met stress om te gaan, en 3) te onderzoeken wanneer studenten zich bevlogen voelen. Tevens is dit onderzoek een verkenning van de variabelen van het Student Wellbeing Model. De onderzoeksuitkomsten dienen aanknopingspunten te bieden voor vervolgonderzoek naar het welzijn van studenten in relatie tot studiesucces. Ten slotte, de inzichten die verkregen worden dienen uiteindelijk bij te dragen aan het tegengaan van een hoge mate van stress (en andere gerelateerde psychische klachten) bij studenten en aan het bevorderen van het welzijn van studenten.
DOCUMENT

Introduction Student success is positively linked to engagement, but negatively linked to emotional exhaustion. Though both constructs have been conceptualized as opposites previously, we hypothesize that students can demonstrate high or low engagement and emotional exhaustion simultaneously. We used quantitative and qualitative data to identify the existence of four student profiles based on engagement and exhaustion scores. Furthermore, we studied how profiles associate to study behaviour, wellbeing and academic achievement, and what risks, protective factors and support requirements students and teachers identify for these profiles. Methods The Student Wellbeing Monitor 2021, developed by Inholland University of Applied Sciences, was used to identify profiles using quadrant analyses based on high and low levels of engagement and emotional exhaustion (n= 1460). Correlation analyses assessed profile specific differences on study behaviours, academic delay, and wellbeing. Semi-structured interviews with students and teachers are currently in progress to further explore the profiles, to identify early signals, and to inspect support requirements. Results The quadrant analysis revealed four profiles: low engagement and low exhaustion (energised-disengaged; 9%), high engagement and low exhaustion (energised-engaged; 15%), low engagement and high exhaustion (exhausted-disengaged; 48%), and high engagement and high exhaustion (exhausted-engaged; 29%). Overall, engaged students demonstrated more active study behaviours and more social connections and interactions with fellow students and teachers. The exhausted students scored higher on depressive symptoms and stress. The exhausted-engaged students reported the highest levels of performance pressure, while the energised-disengaged students had the lowest levels of performance pressure. So far, students and teachers recognise the profiles and have suggested several support recommendations for each profile. Discussion The results show that students can be engaged but at the same time are exhausting themselves. A person-oriented mixed-methods approach helps students and teachers gain awareness of the diversity and needs of students, and improve wellbeing and student success.
MULTIFILE

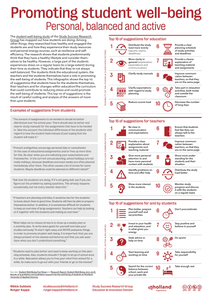
The student well-being study of the Study Success Research Group has mapped out how students are doing. Among other things, they researched how healthy and engaged the students are and how they experience their study resources and personal energy sources, such as resilience and selfefficiency. The research shows that students predominantly think that they have a healthy lifestyle and consider themselves to be healthy. However, a large part of the students experiences stress on a regular basis (to a large extent) during their time as students. This infographic shows the top 10 of suggestions that students have for the students themselves, their teachers and for changes within education/the curriculum that could contribute to reducing stress and could promote the well-being of students.
DOCUMENT